A Comparison between Three Different Automated Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D Immunoassay Methods and Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography
- PMID: 32334467
- PMCID: PMC7445983
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.4.1039
A Comparison between Three Different Automated Total 25-hydroxyvitamin D Immunoassay Methods and Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
Objective: Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin responsible for calcium metabolism and more recently discovered effects. This led to an increase in requests for vitamin D test by clinicians. New automated assays have been introduced for 25-hydroxyvitamin D measurement.
Methods: Results from these new method have to be related to a Standard method to obtain best results for practical usage. In our study, one hundred venous blood samples were analyzed for 25-OH vitamin D on three immunological methods in our lab and correlated with ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method as a reference method.
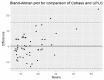
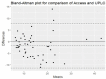
Results: Statistically analysis of results obtained for correlations between the 3 methods against the reference UPLC was done by Spearman's Correlation. It showed positive correlation in all methods with significant p value < 0.001. Differences and biases between methods were evaluated using a Bland-Altman plot and Cohen's Kappa agreement. Best agreement was found in Cobas 6000 followed by the Access2 then comes Architect. Conclusions: All immunoassays can be used in routine 25(OH) D measurements, still some methods are better than others. A clinical laboratory must at least be aware of its method to avoid misinterpretation of results.
Keywords: 25-Hydroxy vitamin D; Vitamin D; Vitamin D method comparison; Vitamin D standardization; vitamin D chromatography.
Figures
References
-
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Comparing methods of measurement- why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet. 1995;346:1085–7. - PubMed
-
- Carter GD. 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a difficult analyte. Clin Chem. 2012;58:486–8. - PubMed
-
- Depreter B, Heijboer AC, Langlois MR. Accuracy of three automated 25- hydroxyvitamin D assays in hemodialysis patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;415:255–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous