Total Atherosclerosis Burden of Baroreceptor-Resident Arteries Independently Predicts Blood Pressure Dipping in Patients With Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 32336234
- PMCID: PMC7682798
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15036
Total Atherosclerosis Burden of Baroreceptor-Resident Arteries Independently Predicts Blood Pressure Dipping in Patients With Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
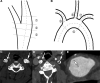
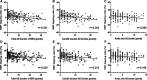
Nighttime blood pressure (BP) generally dips by 10% to 20% of the daytime values, and abnormal BP dipping may affect vascular health independently of BP level. The regulation of BP dipping involves arterial baroreflex, whose receptors mainly reside in carotid sinuses and aortic arch. Atherosclerosis in these baroreceptor-resident arteries (BRAs) is frequent among patients with ischemic stroke (IS) and might impair their BP-regulating capacity. We aimed to examine associations between atherosclerosis of BRA and BP dipping in patients with IS. BP dipping ratio was measured by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring on the sixth day after IS. With computed tomography angiography, atherosclerosis conditions in 10 segments of carotid sinuses and aortic arch were scored and summed as total atherosclerosis burden of BRA. Among the 245 patients with IS, 78.0% had atherosclerosis in BRA. The total AS burden of BRA was negatively correlated with systolic BP dipping ratio (r=-0.331; P<0.001) and diastolic BP dipping ratio (r=-0.225; P<0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, vascular risk factors, 24-hour BP means, cervical and intracranial atherosclerosis scores, the negative correlations still existed (adjusted β, -0.259 [95% CI, -0.416 to -0.102] and adjusted β, -0.178 [95% CI, -0.346 to -0.010], respectively). In conclusion, higher total atherosclerosis burden of BRA was independently indicative of more blunted dipping of systolic BP and diastolic BP in IS. The total atherosclerosis burden of BRA might be important for predicting and managing BP dipping in patients with IS.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; baroreceptor; baroreflex; blood pressure; carotid sinus; dipping; stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating Total Atherosclerosis Burden of Baroreceptor-Resident Arteries after Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease for Identifying Patients with Heavy Coronary Atherosclerosis Burden.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Apr 1;31(4):429-443. doi: 10.5551/jat.64457. Epub 2023 Oct 21. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 37866928 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between Total Atherosclerosis Burden of Baroreceptor-Resident Arteries and ECG Abnormalities after Acute Ischemic Stroke.Brain Sci. 2024 May 16;14(5):505. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14050505. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38790483 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between ambulatory blood pressure and aortic arch atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Apr;221(2):427-31. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.01.010. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22296886 Free PMC article.
-
[Baroreflex and blood pressure variations in borderline hypertension of the young adult].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1991 Aug;84(8):1117-21. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1991. PMID: 1953260 Review. French.
-
Prognostic Effect of the Nocturnal Blood Pressure Fall in Hypertensive Patients: The Ambulatory Blood Pressure Collaboration in Patients With Hypertension (ABC-H) Meta-Analysis.Hypertension. 2016 Apr;67(4):693-700. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06981. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26902495 Review.
Cited by
-
Night-Time Non-dipping Blood Pressure and Heart Rate: An Association With the Risk of Silent Small Vessel Disease in Patients Presenting With Acute Ischemic Stroke.Front Neurol. 2021 Nov 16;12:719311. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.719311. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34867710 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Measurements With High-Sensitivity Troponin and Natriuretic Peptide Levels in SPRINT.Am J Hypertens. 2024 Jul 15;37(8):571-579. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpae035. Am J Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38554284 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluating Total Atherosclerosis Burden of Baroreceptor-Resident Arteries after Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease for Identifying Patients with Heavy Coronary Atherosclerosis Burden.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Apr 1;31(4):429-443. doi: 10.5551/jat.64457. Epub 2023 Oct 21. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 37866928 Free PMC article.
-
Clinic and ambulatory blood pressures, blood pressure phenotypes and mortality in patients with a previous stroke.Hypertens Res. 2024 Sep;47(9):2503-2510. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01760-1. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38918531
-
A Whole-Scope Evaluation of Cervicocephalic Atherosclerotic Burden is Essential to Predict 90-Day Functional Outcome in Large-Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022 Oct 1;29(10):1522-1533. doi: 10.5551/jat.63226. Epub 2021 Nov 20. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2022. PMID: 34803087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parati G, Ochoa JE, Lombardi C, Bilo G. Assessment and management of blood-pressure variability. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013;10:143–155. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.1. - PubMed
-
- Mousa T, el-Sayed MA, Motawea AK, Salama MA, Elhendy A. Association of blunted nighttime blood pressure dipping with coronary artery stenosis in men. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:977–980. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.05.020. - PubMed
-
- Scuteri A, Rovella V, Alunni Fegatelli D, Tesauro M, Gabriele M, Di Daniele N. An operational definition of SHATS (Systemic Hemodynamic Atherosclerotic Syndrome): role of arterial stiffness and blood pressure variability in elderly hypertensive subjects. Int J Cardiol. 2018;263:132–137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.03.117. - PubMed
-
- Di Daniele N, Fegatelli DA, Rovella V, Castagnola V, Gabriele M, Scuteri A. Circadian blood pressure patterns and blood pressure control in patients with chronic kidney disease. Atherosclerosis. 2017;267:139–145. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.10.031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

