Further Development of Near-Infrared Mediated Quantum Dots and Paclitaxel Co-loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier System for Cancer Theragnostic
- PMID: 32336244
- PMCID: PMC7225832
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033820914308
Further Development of Near-Infrared Mediated Quantum Dots and Paclitaxel Co-loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier System for Cancer Theragnostic
Abstract
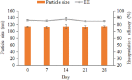
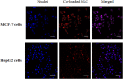
Of colloidal systems, ceteris paribus, nanostructured lipid carriers are second to none in offering a single-unit platform for multifunctional benefits. Quantum dots are known to possess unique properties that make them ideal for imaging purpose and that they may be used for cancer detection. For several decades, paclitaxel has been the most effective drug against a wide range of solid tumours. Theragnostic nanomedicine provides a platform to monitor, evaluate, and individualize treatment in real time. Evaluation of cancer treatment outcome at an early stage therapy is key to increase survival prospects of a patient. Previously, a novel co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers' theragnostic system for parenteral administration was developed. The aim of this study was to further investigate the co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers in order to provide interpretation necessary for preclinical elucidation of the formulation, in part. The co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers were prepared by oil/water emulsification-solvent evaporation technique. In this study, stability and co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers' internalization by MCF 7 and HepG2 cells were investigated. The co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers was stable at 4°C for 1 month. The formulation was successfully internalized by MCF-7 and HepG2 cells. Nevertheless, the co-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier was more apt for MCF-7 cells. This finding affirms the formulation to be the most appropriate for breast cancer treatment. In addition, if taken correctly by a patient for a month, the formulation would give true reflection of the contents' amounts, the factor paramount to appropriate changes in treatment protocol. It can therefore safely be concluded that the co-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier formulation may be potentially an effective theragnostic translational system.
Keywords: cellular uptake; co-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier; stability study; theragnostic; translational system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Near-infrared mediated quantum dots and paclitaxel co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for cancer theragnostic.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Feb 1;150:121-130. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.11.032. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 27907859
-
Targeted Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Delivery of Paclitaxel to Cancer Cells: Preparation, Characterization, and Cell Toxicity.Curr Drug Deliv. 2017;14(8):1189-1200. doi: 10.2174/1567201814666170503143646. Curr Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28472908
-
Facile preparation of biocompatible nanostructured lipid carrier with ultra-small size as a tumor-penetration delivery system.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018 Oct 1;170:355-363. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.06.017. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018. PMID: 29940502
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:598-613. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.055. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29677547 Review.
-
Innovating alopecia treatment: nanostructured lipid carriers as advanced delivery platforms.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6391-6405. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03784-x. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39825967 Review.
Cited by
-
Supramolecular lipid nanoparticles as delivery carriers for non-invasive cancer theranostics.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Oct 28;2:100067. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100067. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanocarriers: Bridging Diagnosis and Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 1;16(9):1158. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091158. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sumer B, Gao J. Theranostic nanomedicine for cancer. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2008;3(2):137–140. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Gambhir SS, Cheon J. Theranostic nanomedicine. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44(10):841–841. - PubMed
-
- Lammers T, Kiessling F, Hennink WE, Storm G. Nanotheranostics and image-guided drug delivery: current concepts and future directions. Mol Pharm. 2010;7(6):1899–1912. - PubMed
-
- Petersen AL, Hansen AE, Gabizon A, Andresen TL. Liposome imaging agents in personalized medicine. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2012;64(13):1417–1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

