The role of Neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: a review
- PMID: 32336282
- PMCID: PMC7183616
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-00569-y
The role of Neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: a review
Abstract
Background: Neurotensin, originally isolated in 1973 has both endocrine and neuromodulator activity and acts through its three main receptors. Their role in promoting tumour cell proliferation, migration, DNA synthesis has been studied in a wide range of cancers. Expression of Neurotensin and its receptors has also been correlated to prognosis and prediction to treatment.
Main body: The effects of NT are mediated through mitogen-activated protein kinases, epidermal growth factor receptors and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinases amongst others. This review is a comprehensive summary of the molecular pathways by which Neurotensin and its receptors act in cancer cells.
Conclusion: Identifying the role of Neurotensin in the underlying molecular mechanisms in various cancers can give way to developing new agnostic drugs and personalizing treatment according to the genomic structure of various cancers. Video abstract.
Keywords: Cancer; Neurotensin; Neurotensin receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

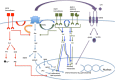
 Role of NT/NTSR1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Role of NT/NTSR1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.  Role of NT/NTSR1 in prostate cancer.
Role of NT/NTSR1 in prostate cancer.  Role of NT/NTSR1 in non small cell lung cancer.
Role of NT/NTSR1 in non small cell lung cancer.  Role of NT/NTSR1 in breast cancer.
Role of NT/NTSR1 in breast cancer.  Role of NT/NTSR1 in glioma.
Role of NT/NTSR1 in glioma.  Role of NT/NTSR1 in glioblastoma multiforme. DAG: diacylglycerol. EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor. ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinases. HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor. HSP27: Heat shock protein 27. IP3: Inositol triphosphate. PKC: Protein kinase C. MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase
Role of NT/NTSR1 in glioblastoma multiforme. DAG: diacylglycerol. EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor. ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinases. HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor. HSP27: Heat shock protein 27. IP3: Inositol triphosphate. PKC: Protein kinase C. MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinaseReferences
-
- Kitabgi P. Targeting neurotensin receptors with agonists and antagonists for therapeutic purposes. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2002;5(5):764–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

