Magnetoencephalography for Schizophrenia
- PMID: 32336407
- PMCID: PMC7241277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nic.2020.01.002
Magnetoencephalography for Schizophrenia
Abstract
Schizophrenia (Sz) is a chronic mental disorder characterized by disturbances in thought (such as delusions and confused thinking), perception (hearing voices), and behavior (lack of motivation). The lifetime prevalence of Sz is between 0.3% and 0.7%, with late adolescence and early adulthood, the peak period for the onset of psychotic symptoms. Causal factors in Sz include environmental and genetic factors and especially their interaction. About 50% of individuals with a diagnosis of Sz have lifelong impairment.
Keywords: Magnetoencephalography; Neuroimaging; Neuroradiologists; Schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
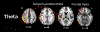
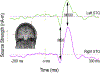
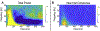

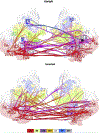
References
-
- Adler LE, Pachtman E, Franks RD, Pecevich M, Waldo MC, & Freedman R (1982). Neurophysiological evidence for a defect in neuronal mechanisms involved in sensory gating in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry, 17(6), 639–654. - PubMed
-
- Alamian G, Hincapie AS, Pascarella A, Thiery T, Combrisson E, Saive AL, … Jerbi K. (2017). Measuring alterations in oscillatory brain networks in schizophrenia with resting-state MEG: State-of-the-art and methodological challenges. Clin Neurophysiol, 128(9), 1719–1736. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.246 - DOI - PubMed
-
- American_Psychiatric_Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders 5th edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Andreasen NC (1997). The evolving concept of schizophrenia: from Kraepelin to the present and future. Schizophr Res, 28(2–3), 105–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

