Inducible Kiss1 knockdown in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus suppressed pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone in male mice
- PMID: 32336702
- PMCID: PMC7470898
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2019-164
Inducible Kiss1 knockdown in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus suppressed pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone in male mice
Abstract
Accumulating evidence suggests that kisspeptin-GPR54 signaling is indispensable for gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)/gonadotropin secretion and consequent reproductive functions in mammals. Conventional Kiss1 knockout (KO) mice and rats are reported to be infertile. To date, however, no study has investigated the effect of inducible central Kiss1 KO/knockdown on pulsatile gonadotropin release in male mammals. Here we report an in vivo analysis of inducible conditional Kiss1 knockdown male mice. The mice were generated by a bilateral injections of either adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors driving Cre recombinase (AAV-Cre) or AAV vectors driving GFP (AAV-GFP, control) into the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC) of Kiss1-floxed male mice, in which exon 3 of the Kiss1 gene were floxed with loxP sites. Four weeks after the AAV-Cre injection, the mice showed a profound decrease in the both number of ARC Kiss1-expressing cells and the luteinizing hormone (LH) pulse frequency. Interestingly, pulsatile LH secretion was apparent 8 weeks after the AAV-Cre injection despite the suppression of ARC Kiss1 expression. The control Kiss1-floxed mice infected with AAV-GFP showed apparent LH pulses and Kiss1 expression in the ARC at both 4 and 8 weeks after the AAV-GFP injection. These results with an inducible conditional Kiss1 knockdown in the ARC of male mice suggest that ARC kisspeptin neurons are responsible for pulsatile LH secretion in male mice, and indicate the possibility of a compensatory mechanism that restores GnRH/LH pulse generation.
Keywords: Adeno-associated virus; Gonadotropin; Gonadotropin-releasing hormone; Kiss1; Metastin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
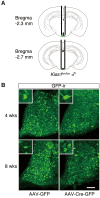


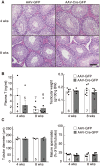
References
-
- Ohkura S, Tsukamura H, Maeda K. Effects of various types of hypothalamic deafferentation on luteinizing hormone pulses in ovariectomized rats. J Neuroendocrinol 1991; 3: 503–508. - PubMed
-
- Gore AC, Terasawa E. Neural circuits regulating pulsatile luteinizing hormone release in the female guinea-pig: opioid, adrenergic and serotonergic interactions. J Neuroendocrinol 2001; 13: 239–248. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi M, Yoshioka K, Kaneko H, Iwamura S, Takahashi T, Suzuki C, Arai S, Wada Y, Itoh S. Measurement of porcine luteinizing hormone concentration in blood by time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. J Vet Med Sci 2007; 69: 1291–1294. - PubMed
-
- Moenter SM, Brand RM, Midgley AR, Karsch FJ. Dynamics of gonadotropin-releasing hormone release during a pulse. Endocrinology 1992; 130: 503–510. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T, Ozawa T, Hoshino K, Mori Y. Changes in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator activity during the estrous cycle in the goat. Neuroendocrinology 1995; 62: 553–561. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

