Rapid Delivery of Gold Nanoparticles into Colon Cancer HT-29 Cells by Electroporation: In-vitro Study
- PMID: 32337183
- PMCID: PMC7166215
- DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.579
Rapid Delivery of Gold Nanoparticles into Colon Cancer HT-29 Cells by Electroporation: In-vitro Study
Abstract
Background: Electroporation has become a routine technique for rapid drug delivery for the treatment of cancer. Because of its simplicity and wide range of application, it has been applied for the transfer of gold-nanoparticles and can facilitate entry into target cancer cells.
Objective: The aim of this study is finding optimal conditions in order to obtain high GNPs- uptake and cell viability by means of electroporation.
Materials and methods: In this in vitro study, exponential electrical pulse with electric field intensity ranging from 0.2 -2 kV/cm, pulse length of 100 µs and the pulse number of 2 was used. Electroporated cell viability was investigated using MTS assay and GNPs-cellular uptake was assayed using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS). Finally, electroporation results were compared with passive method.
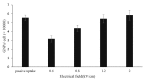
Results: The maximum uptake occurred at 1.2 to 2 kV/cm and passive method happened. The cell viability of 1.2 kV/cm and passive method was about 90%, while the cell viability in 2 kV/cm drastically decreased to 50%. The findings showed that using two pulses of 1.2 kV/cm and 100 µs is a convenient way and surrogate of passive method for internalizing GNPs into cells.
Conclusion: It is concluded that the electroporation-GNPs method could create an opportunistic context for colon cancer therapy. This type of treatment is especially attractive for highly immunogenic types of cancers in patients who are otherwise not surgical candidates or whose tumors are unresectable.
Keywords: Cell Survival; Drug Delivery; Electroporation; Gold Nanoparticles; HT29 Cells.
Copyright: © Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering.
Figures
References
-
- Arab-Bafrani Z, Shahbazi-Gahrouei D, Abbasian M, Fesharaki M. Multiple MTS Assay as the Alternative Method to Determine Survival Fraction of the Irradiated HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells. J Med Signals Sens. 2016;6:112–6. [ PMC Free Article ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shahbazi-Gahrouei D. Novel MR imaging contrast agents for cancer detection. J Res Med Sci. 2009;14:141–7. [ PMC Free Article ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shahbazi-Gahrouei D, Khodamoradi E. Porphyrin-based agents: potential MR imaging contrast agents for colorectal (HT29/219) detection in mice. Journal of Medical Sciences. 2007;7:1015–20. doi: 10.3923/jms.2007.1015.1020. - DOI
-
- Wang Q W, Lu H L, Song C C, Liu H, Xu C G. Radiosensitivity of human colon cancer cell enhanced by immunoliposomal docetaxel. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:4003–7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4003. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith L, Kuncic Z, Ostrikov K, Kumar S. Nanoparticles in cancer imaging and therapy. Journal of Nanomaterials. 2012;2012:10. doi: 10.1155/2012/891318. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources