Hydroalcoholic extract of Achillea millefolium improved blood glucose, liver enzymes and lipid profile compared to metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 32340610
- PMCID: PMC7184710
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-020-01228-4
Hydroalcoholic extract of Achillea millefolium improved blood glucose, liver enzymes and lipid profile compared to metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have reported that herbal extracts may have some protective effect against the complications of diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to investigate the effects of Achillea millefolium hydroalcoholic extract in comparison to metformin on liver damage, lipid abnormality, and glycemic control in diabetic rats.
Methods: Rats were randomly assigned to 7 groups of 10 animals. Diabetes was induced by injection of streptozotocin (STZ) to 4 groups of rats. Three groups of diabetic rats were given 250 mg/kg/day metformin, 25 mg/kg/day Achillea millefolium hydroalcoholic extract, or 100 mg/kg/day of this extract. Two non-diabetic groups were also given either 25 mg/kg/day or 100 mg/kg/day Achillea millefolium extract. Normal control and diabetic control rats received 1 mL/day of normal saline. Treatments were administered through oral gavage for 28 days. At the end, rats were anesthetized with ether and their serum samples were separated in order to measure blood glucose, serum total protein, lipids, and liver enzymes.
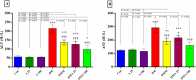
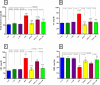
Results: There was a significant reduction in blood glucose, serum liver enzymes, triglycerides, and total- and LDL-cholesterol levels of the Achillea millefolium extract-treated groups compared to the other groups. In addition, there was a significant increment in body weight and HDL-cholesterol serum level in the Achillea millefolium-treated groups.
Conclusion: Achillea millefolium extract compared to metformin reduces lipid abnormality, blood glucose and liver enzymes in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Future clinical studies are warranted to confirm our experimental findings in humans.
Keywords: Achillea millefolium; Blood glucose; Diabetes; Lipid profile; Liver enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sadeghi H, Radmanesh E, TTM A, Mohammadi R, Nazem H. Hypoglycemic effects of Achillea Wilhelmsii in normal and streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. 2009.
-
- Siyahlou S, Barzin G, Entezari M. Review and study of Achillea milefollium essential oil compounds in various stages of development. 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

