Documentation of acute change in mental status in nursing homes highlights opportunity to augment infection surveillance criteria
- PMID: 32340639
- PMCID: PMC8668157
- DOI: 10.1017/ice.2020.77
Documentation of acute change in mental status in nursing homes highlights opportunity to augment infection surveillance criteria
Abstract
Acute change in mental status (ACMS), defined by the Confusion Assessment Method, is used to identify infections in nursing home residents. A medical record review revealed that none of 15,276 residents had an ACMS documented. Using the revised McGeer criteria with a possible ACMS definition, we identified 296 residents and 21 additional infections. The use of a possible ACMS definition should be considered for retrospective nursing home infection surveillance.
Figures
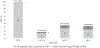
References
-
- Inouye SK. Delirium in older persons. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1157–1165. - PubMed
-
- Kiely DK, Bergmann MA, Murphy KM, Jones RN, Orav EJ, Marcantonio ER. Delirium among newly admitted postacute facility patients: prevalence, symptoms, and severity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2003;58:441–445. - PubMed
-
- Inouye SK, van Dyck CH, Alessi CA, Balkin S, Siegal AP, Horwitz RI. Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med 1990;113:941–948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

