Implementing lung health interventions in low- and middle-income countries: a FRESH AIR systematic review and meta-synthesis
- PMID: 32341109
- PMCID: PMC7409813
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00127-2020
Implementing lung health interventions in low- and middle-income countries: a FRESH AIR systematic review and meta-synthesis
Abstract
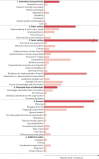
The vast majority of patients with chronic respiratory disease live in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Paradoxically, relevant interventions often fail to be effective particularly in these settings, as LMICs lack solid evidence on how to implement interventions successfully. Therefore, we aimed to identify factors critical to the implementation of lung health interventions in LMICs, and weigh their level of evidence.This systematic review followed Cochrane methodology and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) reporting standards. We searched eight databases without date or language restrictions in July 2019, and included all relevant original, peer-reviewed articles. Two researchers independently selected articles, critically appraised them (using Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP)/Meta Quality Appraisal Tool (MetaQAT)), extracted data, coded factors (following the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR)), and assigned levels of confidence in the factors (via Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation-Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research (GRADE-CERQual)). We meta-synthesised levels of evidence of the factors based on their frequency and the assigned level of confidence (PROSPERO:CRD42018088687).We included 37 articles out of 9111 screened. Studies were performed across the globe in a broad range of settings. Factors identified with a high level of evidence were: 1) "Understanding needs of local users"; 2) ensuring "Compatibility" of interventions with local contexts (cultures, infrastructures); 3) identifying influential stakeholders and applying "Engagement" strategies; 4) ensuring adequate "Access to knowledge and information"; and 5) addressing "Resource availability". All implementation factors and their level of evidence were synthesised in an implementation tool.To conclude, this study identified implementation factors for lung health interventions in LMICs, weighed their level of evidence, and integrated the results into an implementation tool for practice. Policymakers, non-governmental organisations, practitioners, and researchers may use this FRESH AIR (Free Respiratory Evaluation and Smoke-exposure reduction by primary Health cAre Integrated gRoups) Implementation tool to develop evidence-based implementation strategies for related interventions. This could increase interventions' implementation success, thereby optimising the use of already-scarce resources and improving health outcomes.
Copyright ©ERS 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: E.A. Brakema has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D. Vermond has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: H. Pinnock has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Lionis has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: B. Kirenga has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Pham Le has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T. Sooronbaev has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N.H. Chavannes has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R.M.J.J. van der Kleij has nothing to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization Chronic respiratory diseases. www.who.int/respiratory/en/ Data last accessed: January 9, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization Global Surveillance, prevention and control of chronic respiratory diseases: a comprehensive approach, 2007. www.who.int/gard/publications/GARD_Manual/en/ Date last accessed: January 9, 2020.
-
- Halpin DMG, Celli BR, Criner GJ, et al. . It is time for the world to take COPD seriously: a statement from the GOLD board of directors. Eur Respir J 2019; 54: 1900914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
