DLG2 variants in patients with pubertal disorders
- PMID: 32341572
- PMCID: PMC7510947
- DOI: 10.1038/s41436-020-0803-8
DLG2 variants in patients with pubertal disorders
Abstract
Purpose: Impaired function of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons can cause a phenotypic spectrum ranging from delayed puberty to isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH). We sought to identify a new genetic etiology for these conditions.
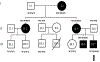
Methods: Exome sequencing was performed in an extended family with autosomal dominant, markedly delayed puberty. The effects of the variant were studied in a GnRH neuronal cell line. Variants in the same gene were sought in a large cohort of individuals with IHH.
Results: We identified a rare missense variant (F900V) in DLG2 (which encodes PSD-93) that cosegregated with the delayed puberty. The variant decreased GnRH expression in vitro. PSD-93 is an anchoring protein of NMDA receptors, a type of glutamate receptor that has been implicated in the control of puberty in laboratory animals. The F900V variant impaired the interaction between PSD-93 and a known binding partner, Fyn, which phosphorylates NMDA receptors. Variants in DLG2 that also decreased GnRH expression were identified in three unrelated families with IHH.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that variants in DLG2/PSD-93 cause autosomal dominant delayed puberty and may also contribute to IHH. The findings also suggest that the pathogenesis involves impaired NMDA receptor signaling and consequently decreased GnRH secretion.
Keywords: DLG2; NMDA receptors; PSD-93; hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; puberty.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
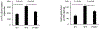
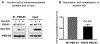
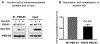
References
-
- Young J, Xu C, Papadakis GE, Acierno JS, Maione L, Hietamäki J, Raivio T, Pitteloud N. Clinical Management of Congenital Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism. Endocr Rev. 2019. 40(2):669–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

