Emergency Responses to Covid-19 Outbreak: Experiences and Lessons from a General Hospital in Nanjing, China
- PMID: 32342164
- PMCID: PMC7184943
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-020-02474-w
Emergency Responses to Covid-19 Outbreak: Experiences and Lessons from a General Hospital in Nanjing, China
Abstract
Background: The novel coronavirus 2019 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused wide dissemination across the world. Global health systems are facing the unprecedented challenges. Here we shared the experiences and lessons in emergency responses and management from our hospital, a government-assigned regional anti-Covid-19 general hospital in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China.
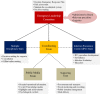
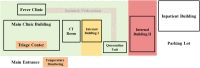
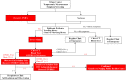
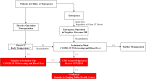
Methods: Our periodic strategies in dealing with Covid-19 were described in detail. An administrative response including the establishment of Emergency Leadership Committee that was in full charge of management was established. Modifications of infrastructure including the Fever Clinic, inpatient ward, outpatient clinic and operation room were carried out. Special arrangements for outpatient services, hospitalization and surgeries were introduced. Medical personnel training and patient educations were performed. Initiations of Covid-19 researches and application of information technology were introduced.
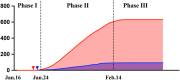
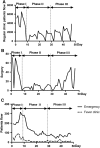
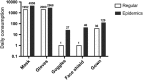
Findings: Since January 16, three cases have been confirmed in our hospital and no healthcare-associated infection was found. During the epidemics, 6.46% staffs suffered depression, 9.87% had anxiety, and 98% were satisfied with the infection control policy. Shortages in staffs and medical consumables, and limitation in space were the obstacles we encountered.
Interpretation: As the cost of in-hospital transmission is unbearable, our experiences and lessons suggested that prompt actions should be taken immediately to decrease or eliminate potential in-hospital transmission. Experience shared herein may be useful for those facilities that are and may encounter Covid-19.
Keywords: Covid-19; Emergency response; Hospital management; Infection prevention and control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Organization WH. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report—59. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 20 March 2020.
-
- Organization WH. Laboratory Biosafety Manual. 2004. https://www.who.int/medical_devices/publications/lab_biosafety_manual/en/. Accessed Jan 16 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

