FDG-PET/CT findings highly suspicious for COVID-19 in an Italian case series of asymptomatic patients
- PMID: 32342191
- PMCID: PMC7184819
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-020-04819-6
FDG-PET/CT findings highly suspicious for COVID-19 in an Italian case series of asymptomatic patients
Abstract
Aim: To illustrate the [18F]FDG-PET/CT findings in patients affected by cancer with clinical diagnosis of Covid-19 METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed the cases of patients who showed pulmonary involvement unrelated to cancer metastases on March 13 and 16 2020. We reviewed the scans, collected medical history, and exposure information.
Results: Among the 13 scans, we identified 5 cases with imaging findings suspicious for viral infection. Peripheral lung consolidations and/or ground-glass opacities in two or more lobes were found. Lung abnormalities displayed increased [18F]FDG uptake (SUVmax 4.3-11.3). All the patients on the day of PET/CT acquisition were asymptomatic, and they did not have fever or cough. In view of the PET/CT findings, home isolation, symptom surveillance, and treatment (in 3/5 patients) were indicated. At 1-week follow-up, 2/5 patients experienced the onset of mild respiratory symptoms.
Conclusions: The [18F]FDG-PET/CT can identify probable Covid-19 disease in the absence or before symptoms onset and can guide patient management. Nuclear medicine staff needs to be aware of the possibility of contact with patients affected by the SARS-CoV-2 infection even if they do not present any symptom. Therefore, safety measures need to be adopted for other patients and hospital staff in order to block the spread of infection.
Keywords: Asymptomatic; COVID-19; Coronavirus; FDG-PET/CT; Imaging; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
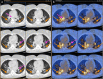


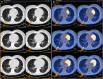

Comment in
-
Incidental SARS-CoV-2-related findings in asymptomatic patients in [18F]-FDG-PET/CT-potential insights.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 Aug;47(9):2068-2069. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04869-w. Epub 2020 May 22. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32444898 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- https://www.assolombarda.it/centro-studi/booklet-italy-lombardy-and-mila..., accessed on Mar 22nd, 2020.
-
- http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it/media-comunicazione/comunicati-stampa... , accessed on Mar 30th, 2020.
-
- Xu Xi, Yu Chengcheng, Qu Jing, Zhang Lieguang, Jiang Songfeng, Huang Deyang, Chen Bihua, Zhang Zhiping, Guan Wanhua, Ling Zhoukun, Jiang Rui, Hu Tianli, Ding Yan, Lin Lin, Gan Qingxin, Luo Liangping, Tang Xiaoping, Liu Jinxin. Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 2020;47(5):1275–1280. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04735-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

