Evaluating the Effectiveness of Social Distancing Interventions to Delay or Flatten the Epidemic Curve of Coronavirus Disease
- PMID: 32343222
- PMCID: PMC7392458
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2608.201093
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Social Distancing Interventions to Delay or Flatten the Epidemic Curve of Coronavirus Disease
Abstract
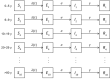
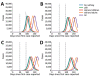
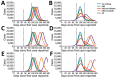
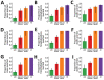
By April 2, 2020, >1 million persons worldwide were infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. We used a mathematical model to investigate the effectiveness of social distancing interventions in a mid-sized city. Interventions reduced contacts of adults >60 years of age, adults 20-59 years of age, and children <19 years of age for 6 weeks. Our results suggest interventions started earlier in the epidemic delay the epidemic curve and interventions started later flatten the epidemic curve. We noted that, while social distancing interventions were in place, most new cases, hospitalizations, and deaths were averted, even with modest reductions in contact among adults. However, when interventions ended, the epidemic rebounded. Our models suggest that social distancing can provide crucial time to increase healthcare capacity but must occur in conjunction with testing and contact tracing of all suspected cases to mitigate virus transmission.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; coronavirus disease; disease transmission; mathematical model; nonpharmaceutical interventions; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; social distancing interventions; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 11 March 2020. [cited 2020 Mar 15]. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re...
-
- Johns Hopkins University and Medicine. Coronavirus resource center. COVID-19 global cases [cited 2020 Apr 2]. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
-
- Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, et al.; Washington State 2019-nCoV Case Investigation Team. Washington State 2019-nCoV Case Investigation Team. First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:929–36. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001191 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Snohomoish County Washington. Local declaration of emergency Snohomish County 2020. Mar 4 [cited 2020 Mar 15]. https://snohomishcountywa.gov/CivicAlerts.aspx
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

