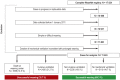
Prolonged Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
- PMID: 32343653
- PMCID: PMC7194302
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2020.0197
Prolonged Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
Abstract
Background: To accommodate the increasing number of patients requiring prolonged weaning from mechanical ventilation, specialized weaning centers have been established for patients in whom weaning on the intensive care unit (ICU) was unsuccessful.
Methods: This study aimed to determine both the outcome of treatment and the factors associated with prolonged weaning in patients who were transferred from the ICU to specialized weaning centers in Germany during the period 2011 to 2015, based on a nationwide registry covering all specialized weaning centers currently going through the process of accreditation by the German Respiratory Society.
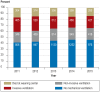
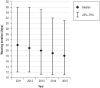
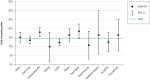
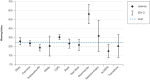
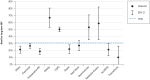
Results: Of 11 424 patients, 7346 (64.3%) were successfully weaned, of whom 2236 were switched to long-term non-invasive ventilation; 1658 (14.5%) died in the weaning unit; and 2420 (21.2%) could not be weaned. The duration of weaning decreased significantly from 22 to 18 days between 2011 and 2015 (p <0.0001). Multivariate analysis revealed that the factor most strongly associated with in-hospital mortality was advanced age (odds ratio [OR] 11.07, 95% confidence interval [6.51; 18.82], p <0.0001). The need to continue with invasive ventilation was most strongly associated with the duration mechanical ventilation prior to transfer from the ICU (OR 4.73 [3.25; 6.89]), followed by a low body mass index (OR 0.38 [0.26; 0.58]), pre-existing neuromuscular disorders (OR 2.98 [1.88; 4.73]), and advanced age (OR 2.96 [1.87; 4.69]) (each p <0.0001).
Conclusion: Weaning duration has decreased over time, but prolonged weaning is still unsuccessful in one third of patients.Overall, the results warrant the establishment of specialized weaning centers. Variables associated with death and weaningfailure can be integrated into ICU decision-making processes.
Figures
References
-
- McConville JF, Kress JP. Weaning patients from the ventilator. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2233–2239. - PubMed
-
- Boles JM, Bion J, Connors A, et al. Weaning from mechanical ventilation. Eur Respir J. 2007;29:1033–1056. - PubMed
-
- Epstein SK, Ciubotaru RL. Independent effects of etiology of failure and time to reintubation on outcome for patients failing extubation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158:489–493. - PubMed
-
- Thille AW, Richard J-CM, Brochard L. The decision to extubate in the intensive care unit. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:1294–1302. - PubMed
-
- Peñuelas O, Frutos-Vivar F, Fernández C, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of ventilated patients according to time to liberation from mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184:430–437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

