Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32344321
- PMCID: PMC7194648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370
Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19
Abstract
Background: The inflammatory response plays a critical role in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and inflammatory cytokine storm increases the severity of COVID-19.
Objective: To investigate the ability of interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), and procalcitonin (PCT) to predict mild and severe cases of COVID-19.
Study design: This retrospective cohort study included 140 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 from January 18, 2020, to March 12, 2020. The study population was divided into two groups according to disease severity: a mild group (MG) (n = 107) and a severe group (SG) (n = 33). Data on demographic characteristics, baseline clinical characteristics, and the levels of IL-6, CRP, and PCT on admission were collected.
Results: Among the 140 patients, the levels of IL-6, CRP, and PCT increased in 95 (67.9 %), 91 (65.0 %), and 8 (5.7 %) patients on admission, respectively. The proportion of patients with increased IL-6, CRP, and PCT levels was significantly higher in the SG than in the MG. Cox proportional hazard model showed that IL-6 and CRP could be used as independent factors to predict the severity of COVID-19. Furthermore, patients with IL-6 > 32.1 pg/mL or CRP > 41.8 mg/L were more likely to have severe complications.
Conclusion: The serum levels of IL-6 and CRP can effectively assess disease severity and predict outcome in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; COVID-19; Interleukin-6; Procalcitonin; Prognosis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19”.
Figures


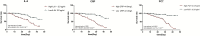
References
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wei W., Xie X., Yin W., Lin H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang D., Hu B., Hu C., Zhu F., Liu X., Zhang J., Wang B., Xiang H., Cheng Z., Xiong Y., Zhao Y., Li Y., Wang X., Peng Z. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323:1061–1069. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Health and Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis and Treatment of Pneumonia of New Coronavirus Infection (Trial Version 7). (2020-03-03), http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19....
-
- Yang P.H., Ding Y.B., Xu Z., Pu R., Li P., Yan J., Liu J.L., Meng F.P., Huang L., Shi L., Jiang T.J., Qin E.Q., Zhao M., Zhang D.W., Zhao P., Yu L.X., Wang Z.H., Hong Z.X., Xiao Z.H., Xi Q., Zhao D.X., Yu P., Zhu C.Z., Chen Z., Zhang S.G., Ji J.S., Cao G.W., Wang F.S. Epidemiological and clinical features of COVID-19 patients with and without pneumonia in Beijing, China. Medrxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.28.20028068. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

