Building, Hosting and Recruiting: A Brief Introduction to Running Behavioral Experiments Online
- PMID: 32344671
- PMCID: PMC7226161
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10040251
Building, Hosting and Recruiting: A Brief Introduction to Running Behavioral Experiments Online
Abstract
Researchers have ample reasons to take their experimental studies out of the lab and into the online wilderness. For some, it is out of necessity, due to an unforeseen laboratory closure or difficulties in recruiting on-site participants. Others want to benefit from the large and diverse online population. However, the transition from in-lab to online data acquisition is not trivial and might seem overwhelming at first. To facilitate this transition, we present an overview of actively maintained solutions for the critical components of successful online data acquisition: creating, hosting and recruiting. Our aim is to provide a brief introductory resource and discuss important considerations for researchers who are taking their first steps towards online experimentation.
Keywords: behavioral sciences; online experiments; online methods; remote testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
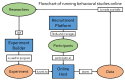

References
-
- Coronavirus Confirmed as Pandemic. [(accessed on 24 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-51839944.
-
- Colleges and Universities across the US Are Canceling In-Person Classes due to Coronavirus—CNN. [(accessed on 24 March 2020)]; Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/2020/03/09/us/coronavirus-university-college-cla....
-
- Birnbaum M. Introduction to Behavioral Research on the Internet. Prentice Hall; Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: 2001.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

