Detection of Platelet-Activating Antibodies Associated with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 32344682
- PMCID: PMC7230370
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9041226
Detection of Platelet-Activating Antibodies Associated with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
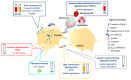
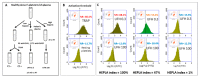
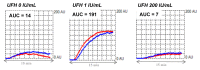
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a prothrombotic immune drug reaction caused by platelet-activating antibodies that in most instances recognize platelet factor 4 (PF4)/polyanion complexes. Platelet activation assays (i.e., functional assays) are more specific than immunoassays, since they are able to discern clinically relevant heparin-induced antibodies. All functional assays used for HIT diagnosis share the same principle, as they assess the ability of serum/plasma from suspected HIT patients to activate fresh platelets from healthy donors in the presence of several concentrations of heparin. Depending on the assay, donors' platelets are stimulated either in whole blood (WB), platelet-rich plasma (PRP), or in a buffer medium (washed platelets, WP). In addition, the activation endpoint studied varies from one assay to another: platelet aggregation, membrane expression of markers of platelet activation, release of platelet granules. Tests with WP are more sensitive and serotonin release assay (SRA) is considered to be the current gold standard, but functional assays suffer from certain limitations regarding their sensitivity, specificity, complexity, and/or accessibility. However, the strict adherence to adequate preanalytical conditions, the use of selected platelet donors and the inclusion of positive and negative controls in each run are key points that ensure their performances.
Keywords: diagnosis; functional assays; heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
C. Pouplard reports a cooperation contract between Stago and the University of Tours, personal fees from Sobi and Roche, and non-financial support from Sobi, Shire, CSL Behring, Roche, Octapharma, all outside the present work. C. Vayne reports a cooperation contract between Stago and the University of Tours and non-financial support from Shire, Sobi, Roche, CSL Behring, Takeda, all outside the present work. F. Mullier reports institutional fees from Stago, Werfen, Nodia, Sysmex, and Bayer. He also reports speaker fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb-Pfizer, Stago, Werfen, and Aspen, all outside the present work. T. Lecompte reports a cooperation contract with Stago, outside the present work.
Figures

References
-
- Pouplard C., Iochmann S., Renard B., Herault O., Colombat P., Amiral J., Gruel Y. Induction of monocyte tissue factor expression by antibodies to heparin-platelet factor 4 complexes developed in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2001;97:3300–3302. doi: 10.1182/blood.V97.10.3300. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

