ExpansionHunter Denovo: a computational method for locating known and novel repeat expansions in short-read sequencing data
- PMID: 32345345
- PMCID: PMC7187524
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02017-z
ExpansionHunter Denovo: a computational method for locating known and novel repeat expansions in short-read sequencing data
Abstract
Repeat expansions are responsible for over 40 monogenic disorders, and undoubtedly more pathogenic repeat expansions remain to be discovered. Existing methods for detecting repeat expansions in short-read sequencing data require predefined repeat catalogs. Recent discoveries emphasize the need for methods that do not require pre-specified candidate repeats. To address this need, we introduce ExpansionHunter Denovo, an efficient catalog-free method for genome-wide repeat expansion detection. Analysis of real and simulated data shows that our method can identify large expansions of 41 out of 44 pathogenic repeats, including nine recently reported non-reference repeat expansions not discoverable via existing methods.
Keywords: Fragile X syndrome; Friedreich ataxia; Genome-wide analysis; Huntington disease; Myotonic dystrophy type 1; Repeat expansions; Short tandem repeats; Whole-genome sequencing data.
Conflict of interest statement
ED, SC, VGG, AG, BL, RJT, DRB, and MAE are or were employees of Illumina, Inc., a public company that develops and markets systems for genetic analysis.
Figures
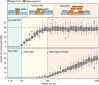

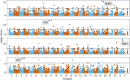

References
-
- Gudbjartsson DF, Helgason H, Gudjonsson SA, Zink F, Oddson A, Gylfason A, et al. Large-scale whole-genome sequencing of the Icelandic population. Nat Genet. 2015;47:435–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

