Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with severe covid-19 with diabetes
- PMID: 32345579
- PMCID: PMC7222577
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001343
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with severe covid-19 with diabetes
Abstract
Objective: This study explores the clinical characteristics of patients with diabetes with severe covid-19, and the association of diabetes with survival duration in patients with severe covid-19.
Research design and methods: In this single-center, retrospective, observational study, the clinical and laboratory characteristics of 193 patients with severe covid-19 were collected. 48 patients with severe covid-19 had diabetes, and 145 patients (ie, the controls) did not have diabetes. A severe case was defined as including at least one of the following criteria: (1) Respiratory rate >30/min. (2) Oxygen saturation ≤93%. (3) PaO2/FiO2≤300 mm Hg. (4) Patients, either with shock or respiratory failure, requiring mechanical ventilation, or combined with other organ failure, requiring admission to intensive care unit (ICU).
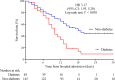
Results: Of 193 patients with severe covid-19, 48 (24.9%) had diabetes. Compared with patients with severe covid-19 without diabetes, patients with diabetes were older, susceptible to receiving mechanical ventilation and admission to ICU, and had higher mortality. In addition, patients with severe covid-19 with diabetes had higher levels of leukocyte count, neutrophil count, high-sensitivity C reaction protein, procalcitonin, ferritin, interleukin (IL) 2 receptor, IL-6, IL-8, tumor necrosis factor α, D-dimer, fibrinogen, lactic dehydrogenase and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide. Among patients with severe covid-19 with diabetes, more non-survivors were men (30 (76.9%) vs 9 (23.1%)). Non-survivors had severe inflammatory response, and cardiac, hepatic, renal and coagulation impairment. Finally, the Kaplan-Meier survival curve showed a trend towards poorer survival in patients with severe covid-19 with diabetes than patients without diabetes. The HR was 1.53 (95% CI 1.02 to 2.30; p=0.041) after adjustment for age, sex, hypertension, cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease by Cox regression. The median survival durations from hospital admission in patients with severe covid-19 with and without diabetes were 10 days and 18 days, respectively.
Conclusion: The mortality rate in patients with severe covid-19 with diabetes is considerable. Diabetes may lead to an increase in the risk of death.
Keywords: adult diabetes.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diabetes and covid-19: a global health challenge.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 Apr;8(1):e001450. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001450. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 32345580 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical