PTX3 modulates the immunoflogosis in tumor microenvironment and is a prognostic factor for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32345771
- PMCID: PMC7202504
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103169
PTX3 modulates the immunoflogosis in tumor microenvironment and is a prognostic factor for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
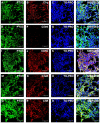
Pentraxin-3 (PTX3) belongs to the pentraxine family, innate immune regulators involved in angiogenesis, proliferation and immune escape in cancer. Here, we evaluated PTX3 tissue expression and serum levels as biomarkers of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and analyzed the possible role of complement system activation on tumor site. A 10-year retrospective cohort study including patients undergoing nephrectomy for ccRCC was also performed. PTX3 expression was elevated in both neoplastic renal cell lines and tissues, while it was absent in both normal renal proximal tubular cells (HK2) and normal renal tissues. Analysis of complement system activation on tumor tissues showed the co-expression of PTX3 with C1q, C3aR, C5R1 and CD59, but not with C5b-9 terminal complex. RCC patients showed higher serum PTX3 levels as compared to non-neoplastic patients (p<0.0001). Higher PTX3 serum levels were observed in patients with higher Fuhrman grade (p<0.01), lymph node (p<0.0001), and visceral metastases (p<0.001). Patients with higher PTX3 levels also showed significantly lower survival rates (p=0.002). Our results suggest that expression of PTX3 can affect the immunoflogosis in the ccRCC microenvironment, by activating the classical pathway of CS (C1q) and releasing pro-angiogenic factors (C3a, C5a). The up-regulation of CD59 also inhibits the complement-mediated cellular lysis.
Keywords: biomarker; complement system; pentraxin 3; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- de Martino M, Gigante M, Cormio L, Prattichizzo C, Cavalcanti E, Gigante M, Ariano V, Netti GS, Montemurno E, Mancini V, Battaglia M, Gesualdo L, Carrieri G, Ranieri E. JAK3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: mutational screening and clinical implications. Urol Oncol. 2013; 31:930–37. 10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

