A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of daily cannabidiol for the treatment of canine osteoarthritis pain
- PMID: 32345916
- PMCID: PMC7584779
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001896
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of daily cannabidiol for the treatment of canine osteoarthritis pain
Abstract
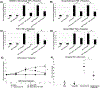
Over the last 2 decades, affirmative diagnoses of osteoarthritis (OA) in the United States have tripled due to increasing rates of obesity and an aging population. Hemp-derived cannabidiol (CBD) is the major nontetrahydrocannabinol component of cannabis and has been promoted as a potential treatment for a wide variety of disparate inflammatory conditions. Here, we evaluated CBD for its ability to modulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in vitro and in murine models of induced inflammation and further validated the ability of a liposomal formulation to increase bioavailability in mice and in humans. Subsequently, the therapeutic potential of both naked and liposomally encapsulated CBD was explored in a 4-week, randomized placebo-controlled, double-blinded study in a spontaneous canine model of OA. In vitro and in mouse models, CBD significantly attenuated the production of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α while elevating levels of anti-inflammatory IL-10. In the veterinary study, CBD significantly decreased pain and increased mobility in a dose-dependent fashion among animals with an affirmative diagnosis of OA. Liposomal CBD (20 mg/day) was as effective as the highest dose of nonliposomal CBD (50 mg/day) in improving clinical outcomes. Hematocrit, comprehensive metabolic profile, and clinical chemistry indicated no significant detrimental impact of CBD administration over the 4-week analysis period. This study supports the safety and therapeutic potential of hemp-derived CBD for relieving arthritic pain and suggests follow-up investigations in humans are warranted.
Copyright © 2020 International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
Institutional policy requires WKD, MMH, and VK to declare their ownership stakes in Diakonos Research, Ltd, an unrelated immuno-oncology company. Additionally, MMH is a paid scientific advisor for Medterra CBD. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



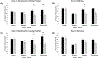

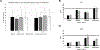
References
-
- Bannwarth B Acetaminophen or NSAIDs for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2006;20(1):117–129. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shabat S, Hanus LO, Katzavian G, Gallily R. New cannabidiol derivatives: synthesis, binding to cannabinoid receptor, and evaluation of their antiinflammatory activity. J Med Chem 2006;49(3):1113–1117. - PubMed
-
- Borrelli F, Aviello G, Romano B, Orlando P, Capasso R, Maiello F, Guadagno F, Petrosino S, Capasso F, Di Marzo V, Izzo AA. Cannabidiol, a safe and non-psychotropic ingredient of the marijuana plant Cannabis sativa, is protective in a murine model of colitis. J Mol Med (Berl) 2009;87(11):1111–1121. - PubMed
-
- Brandt KD, Braunstein EM, Visco DM, O’Connor B, Heck D, Albrecht M. Anterior (cranial) cruciate ligament transection in the dog: a bona fide model of osteoarthritis, not merely of cartilage injury and repair. J Rheumatol 1991;18(3):436–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

