Indigofera oblongifolia as a fight against hepatic injury caused by murine trypanosomiasis
- PMID: 32346351
- PMCID: PMC7182791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.11.038
Indigofera oblongifolia as a fight against hepatic injury caused by murine trypanosomiasis
Abstract
Trypanosoma evansi is a hazardous pathogenic parasite infecting a broad variety of livestock and affects wildlife worldwide. Trypanosoma evansi has gained resistance to most drugs used; therefore, it requires alternative medicines. The objective of this research was to investigate the impact of Indigofera oblongifolia leaf extract (IE) on T. evansi-induced hepatic injury. Mice were once infected with 1000 T. evansi. The treated group was gavaged with 100 mg/Kg IE after infection. Histological and biochemical changes in mice hepatic tissue were studied. Also, the oxidative damage in the liver was evaluated through determining the level of glutathione (GSH), Malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO) and catalase (CAT) markers. IE was able to suppress the induced parasitemia due to infection. Also, IE improved the histological liver architecture. Furthermore, the liver enzymes, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity were improved after IE mice were treated. IE protects against hepatic damage caused by trypanosomiasis in mice. Further studies are needed to isolate the active compounds in IE and to monitor these compunds' ameliorative function.
Keywords: Indigofera oblongifolia; Liver damage; Mouse; Oxidative status; Trypanosoma.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Figures
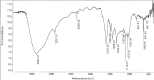
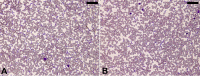


References
-
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Anosa V.O. Haematological and biochemical changes in human and animal trypanosomiasis. Part II. Rev. Elev. Med. Vet. Pays. Trop. 1988;41:151–164. - PubMed
-
- Biswas D., Choudhury A., Misra K.K. Histopathology of Trypanosoma (Trypanozoon) evansi infection in bandicoot rat. I. Visceral organs. Exp. Parasitol. 2001;99:148–159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

