Prediction of median survival time in sepsis patients by the SOFA score combined with different predictors
- PMID: 32346543
- PMCID: PMC7175770
- DOI: 10.1093/burnst/tkz006
Prediction of median survival time in sepsis patients by the SOFA score combined with different predictors
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is the leading cause of intensive care unit (ICU) admission. The purpose of this study was to explore the prognostic value of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, the Acute Physiological and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score, and procalcitonin (PCT), albumin (ALB), and lactate (LAC) levels in patients with sepsis.
Methods: Consecutive adult patients with suspected or documented sepsis at ICU admission were recruited. Their basic vital signs and related auxiliary examinations to determine their PCT and ALB levels and APACHE II score were recorded at ICU admission, and their LAC levels and SOFA scores were recorded for one week after admission. The influence of these variables on hospital mortality was evaluated. Logistic regression was used to derive the Sepsis Hospital Mortality Score (SHMS), a prediction equation describing the relationship between predictors and hospital mortality. The median survival time was calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method. In the validation group, the kappa value was calculated to evaluate the stability of the derived formula.
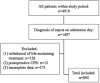
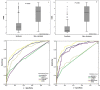
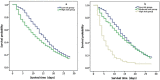
Results: This study included 894 sepsis patients admitted to 18 ICUs in 16 tertiary hospitals. Patients were randomly assigned to an experimental group (626 cases) and validation group (258 cases). In addition, a nonsurvival group (248 patients) of the experimental group was established according to the outcome at the time of discharge. The hospital mortality rate in the experimental group was 39.6% (248/626). Univariate and multivariate regression analyses revealed that the APACHE II score (odds ratio [OR] = 1.178), △SOFA (OR = 1.186), △LAC (OR = 1.157), and SOFA mean score (OR = 1.086) were independently associated with hospital mortality. The SHMS was calculated as logit(p) = 4.715 - (0.164 × APACHE II) - (0.171 × △SOFA) - (0.145 × △LAC) - (0.082 × SOFA mean). A receiver operating characteristic curve was constructed to further investigate the accuracy of the SHMS, with an area under the curve of 0.851 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.821-0.882; p < 0.001) for hospital mortality. In the low-risk group and high-risk groups, the corresponding median survival times were 15 days and 11 days, respectively.
Conclusion: The APACHE II score, △SOFA, △LAC and SOFA mean score were independently associated with hospital mortality in sepsis patients and accurately predicted the hospital mortality rate and median survival time. Data on the median survival time in sepsis patients could be provided to clinicians to assist in the rational use of limited medical resources by facilitating prudent resource allocation.
Trial registration: ChiCTR-ECH-13003934, retrospectively registered on August 03, 2013.
Keywords: APACHE II; Acute Physiological and Chronic Health Evaluation II; Lactate; Mortality; SOFA; Sepsis; Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SOFA Score in relation to Sepsis: Clinical Implications in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognostic Assessment.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 10;2022:7870434. doi: 10.1155/2022/7870434. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9856196. doi: 10.1155/2023/9856196. PMID: 35991153 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
[Lactic acid, lactate clearance and procalcitonin in assessing the severity and predicting prognosis in sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Apr;32(4):449-453. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200129-00086. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32527351 Chinese.
-
[Prognostic value of Charlson weighted index of comorbidities combined with sequential organ failure assessment score and procalcitonin in patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Nov;31(11):1335-1339. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.11.005. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31898562 Chinese.
-
Application Prospect of the SOFA Score and Related Modification Research Progress in Sepsis.J Clin Med. 2023 May 16;12(10):3493. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103493. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saikosaponin-d Alleviates Renal Inflammation and Cell Apoptosis in a Mouse Model of Sepsis via TCF7/FOSL1/Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Inhibition.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Sep 24;41(10):e0033221. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00332-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34309413 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical Capability in Distinguishing Severities of Sepsis via Serum Lactate: A Network Meta-Analysis.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 17;12(2):447. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020447. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening and Application of DNA Aptamers for Heparin-Binding Protein.Molecules. 2024 Apr 10;29(8):1717. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081717. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675537 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of thiamine, vitamin C and hydrocortisone in treating patients with sepsis and septic shock: a meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Burns Trauma. 2021 Dec 6;9:tkab040. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkab040. eCollection 2021. Burns Trauma. 2021. PMID: 34901285 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Interleukin-6 in Emergency Department Sepsis Patients.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Sep 21;15:5557-5566. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S384351. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36172624 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

