"Meds-in-Hand" Intervention to Reduce Critical Process Delays in Pediatric Human Immunodeficiency Virus Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
- PMID: 32347312
- PMCID: PMC7996639
- DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piaa033
"Meds-in-Hand" Intervention to Reduce Critical Process Delays in Pediatric Human Immunodeficiency Virus Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
Abstract
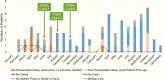
Pediatric human immunodeficiency virus post-exposure prophylaxis is frequently indicated, but delays in medication receipt are common. Using plan-do-study-act cycles, we developed a multidisciplinary collaboration to reduce critical process delays in our pediatric emergency department. Interruptions decreased from a median 1 per month pre-intervention to zero per month during the intervention.
Keywords: human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); pediatric HIV; post-exposure prophylaxis; quality improvement.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Fajman N, Wright R. Use of antiretroviral HIV post-exposure prophylaxis in sexually abused children and adolescents treated in an inner-city pediatric emergency department. Child Abuse Negl 2006; 30:919–27. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services. Updated guidelines for antiretroviral postexposure prophylaxis after sexual, injection drug use, or other nonoccupational exposure to HIV—United States, 2016. 2016; Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/programresources/cdc-hiv-npep-guidelines.pdf. Accessed December 6, 2019.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. 2015. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/default.htm. Accessed December 6, 2019.
-
- Babl FE, Cooper ER, Damon B, et al. . HIV postexposure prophylaxis for children and adolescents. Am J Emerg Med 2000; 18:282–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

