Genistin: A Novel Potent Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Lipogenic Agent
- PMID: 32349444
- PMCID: PMC7248826
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25092042
Genistin: A Novel Potent Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Lipogenic Agent
Erratum in
-
Correction: Choi et al. Genistin: A Novel Potent Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Lipogenic Agent. Molecules 2020, 25, 2042.Molecules. 2024 Feb 4;29(3):714. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030714. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338490 Free PMC article.
Abstract
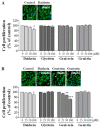
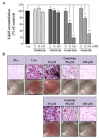
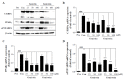
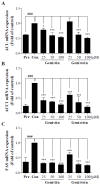
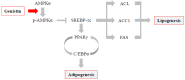
Soy isoflavones are popular ingredients with anti-adipogenic and anti-lipogenic properties. The anti-adipogenic and anti-lipogenic properties of genistein are well-known, but those of genistin and glycitein remain unknown, and those of daidzein are characterized by contrasting data. Therefore, the purpose of our study was to investigate the effects of daidzein, glycitein, genistein, and genistin on adipogenesis and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Proliferation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes was unaffected by genistin and glycitein, but it was affected by 50 and 100 µM genistein and 100 µM daidzein for 48 h. Among the four isoflavones, only 50 and 100 µM genistin and genistein markedly suppressed lipid accumulation during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells through a similar signaling pathway in a dose-dependent manner. Genistin and genistein suppress adipocyte-specific proteins and genes, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα), and adipocyte binding protein 2 (aP2)/fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4), and lipogenic enzymes such as ATP citrate lyase (ACL), acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), and fatty acid synthase (FAS). Both isoflavones also activate AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα), an essential factor in adipocyte differentiation, and inhibited sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1c (SREBP-1c). These results indicate that genistin is a potent anti-adipogenic and anti-lipogenic agent.
Keywords: anti-adipogenesis; anti-lipogenesis; genistin; soy isoflavones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Muir L.A., Neeley C.K., Meyer K.A., Baker N.A., Brosius A.M., Washabaugh A.R., Varban O.A., Finks J.F., Zamarron B.F., Flesher C.G., et al. Adipose tissue fibrosis, hypertrophy, and hyperplasia: Correlations with diabetes in human. Obesity. 2016;24:597–605. doi: 10.1002/oby.21377. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Z.D., Rosen E.D., Brun R., Hauser S., Adelmant G., Troy A.E., McKeon C., Darlington G.J., Spiegelman B.M. Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell. 1999;3:151–158. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80306-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 118035-3/Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food,Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries(IPET) through High Value-added Food Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA)
- E0164500-05/Main Research Program of the Korea Food Research Institute and 2017 Ottogi Foundation research program.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

