PTEN-induced kinase 1-induced dynamin-related protein 1 Ser637 phosphorylation reduces mitochondrial fission and protects against intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury
- PMID: 32351292
- PMCID: PMC7183859
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1758
PTEN-induced kinase 1-induced dynamin-related protein 1 Ser637 phosphorylation reduces mitochondrial fission and protects against intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury
Abstract
Background: Intestinal ischemia reperfusion (I/R) occurs in various diseases, such as trauma and intestinal transplantation. Excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and subsequent apoptotic cell death in intestinal epithelia are important causes of I/R injury. PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1) and phosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) are critical regulators of ROS and apoptosis. However, the correlation of PINK1 and DRP1 and their function in intestinal I/R injury have not been investigated. Thus, examining the PINK1/DRP1 pathway may help to identify a protective strategy and improve the patient prognosis.
Aim: To clarify the mechanism of the PINK1/DRP1 pathway in intestinal I/R injury.
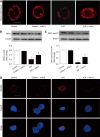
Methods: Male C57BL/6 mice were used to generate an intestinal I/R model via superior mesenteric artery occlusion followed by reperfusion. Chiu's score was used to evaluate intestinal mucosa damage. The mitochondrial fission inhibitor mdivi-1 was administered by intraperitoneal injection. Caco-2 cells were incubated in vitro in hypoxia/reoxygenation conditions. Small interfering RNAs and overexpression plasmids were transfected to regulate PINK1 expression. The protein expression levels of PINK1, DRP1, p-DRP1 and cleaved caspase 3 were measured by Western blotting. Cell viability was evaluated using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and cell apoptosis was analyzed by TUNEL staining. Mitochondrial fission and ROS were tested by MitoTracker and MitoSOX respectively.
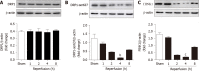
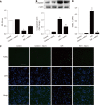
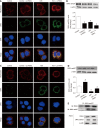
Results: Intestinal I/R and Caco-2 cell hypoxia/reoxygenation decreased the expression of PINK1 and p-DRP1 Ser637. Pretreatment with mdivi-1 inhibited mitochondrial fission, ROS generation, and apoptosis and ameliorated cell injury in intestinal I/R. Upon PINK1 knockdown or overexpression in vitro, we found that p-DRP1 Ser637 expression and DRP1 recruitment to the mitochondria were associated with PINK1. Furthermore, we verified the physical combination of PINK1 and p-DRP1 Ser637.
Conclusion: PINK1 is correlated with mitochondrial fission and apoptosis by regulating DRP1 phosphorylation in intestinal I/R. These results suggest that the PINK1/DRP1 pathway is involved in intestinal I/R injury, and provide a new approach for prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Dynamin-related protein 1 ser637; Intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury; Mitochondrial fission; PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; Phosphorylation.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Acosta S. Epidemiology of mesenteric vascular disease: clinical implications. Semin Vasc Surg. 2010;23:4–8. - PubMed
-
- Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC, Seifalian AM. Ischemia-reperfusion injury of the intestine and protective strategies against injury. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49:1359–1377. - PubMed
-
- Stone JR, Wilkins LR. Acute mesenteric ischemia. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;18:24–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

