Tumor Microenvironment: Extracellular Matrix Alterations Influence Tumor Progression
- PMID: 32351878
- PMCID: PMC7174611
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00397
Tumor Microenvironment: Extracellular Matrix Alterations Influence Tumor Progression
Abstract
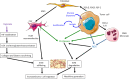
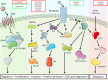
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is composed of various cell types embedded in an altered extracellular matrix (ECM). ECM not only serves as a support for tumor cell but also regulates cell-cell or cell-matrix cross-talks. Alterations in ECM may be induced by hypoxia and acidosis, by oxygen free radicals generated by infiltrating inflammatory cells or by tumor- or stromal cell-secreted proteases. A poorer diagnosis for patients is often associated with ECM alterations. Tumor ECM proteome, also named cancer matrisome, is strongly altered, and different ECM protein signatures may be defined to serve as prognostic biomarkers. Collagen network reorganization facilitates tumor cell invasion. Proteoglycan expression and location are modified in the TME and affect cell invasion and metastatic dissemination. ECM macromolecule degradation by proteases may induce the release of angiogenic growth factors but also the release of proteoglycan-derived or ECM protein fragments, named matrikines or matricryptins. This review will focus on current knowledge and new insights in ECM alterations, degradation, and reticulation through cross-linking enzymes and on the role of ECM fragments in the control of cancer progression and their potential use as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
Keywords: cancer; extracellular matrix; integrins; matrikines; microenvironment; proteases.
Copyright © 2020 Brassart-Pasco, Brézillon, Brassart, Ramont, Oudart and Monboisse.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

