Assessment of chromosome stability in boars
- PMID: 32352977
- PMCID: PMC7192426
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231928
Assessment of chromosome stability in boars
Abstract
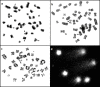
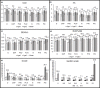
Chromosome instability adversely affects animal fertility and reproduction. Analysis of instability can be a valuable diagnostic tool. Helpful tests for assessment of instabilities include the sister chromatid exchange assay, identification of fragile sites, the bleomycin assay and the comet assay. These techniques can be used to assess and compare the chromosome stability of individual breeds of animals. The aim of the study was to assess chromosome stability in boars: Duroc, Duroc x Pietrain and Pietrain x Duroc crossbreds, Polish Large White, and the Neckar, P76 and PIC lines. The study assessed the chromosome stability of boars. The distribution of instabilities in individual breeds was varied. The average frequency of chromatid exchange was 4.8 ± 1.5, while that of fragile sites was 3.9 ± 1.4. The mean level of DNA damage (% tail DNA) was 9.4 ± 8.3, while in the bleomycin assay b/c and %AM were 0.6 ± 0.7 and 44.4 ± 4.1. A higher rate of instability was found in older individuals than in younger ones. The cytogenetic assays used to identify various forms of chromosome instability can be used to evaluate boars intended for breeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The author confirms that there is no known conflict of interest associated with this publication
Figures
References
-
- Nino-Soto M, King WA. Genetic factors that affect normal reproduction and fertility in domestic cattle. Med Vet Du Quebec Can. 2004;34: 71–72.
-
- Iannuzzi L. Cytogenetics in animal production. Ital J Anim Sci. 2007;6: 713–715. 10.4081/ijas.2007.1s.23 - DOI
-
- Khatun MR, Arifuzzaman Md, Ashraf A. Karyotype for identification of genetic abnormalities in cattle. Asian J Anim Vet Adv. 2011;6: 117–125.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

