Delays in hospital admissions in patients with fractures across 18 low-income and middle-income countries (INORMUS): a prospective observational study
- PMID: 32353318
- PMCID: PMC10809849
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30067-X
Delays in hospital admissions in patients with fractures across 18 low-income and middle-income countries (INORMUS): a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: The Lancet Commission on Global Surgery established the Three Delays framework, categorising delays in accessing timely surgical care into delays in seeking care (First Delay), reaching care (Second Delay), and receiving care (Third Delay). Globally, knowledge gaps regarding delays for fracture care, and the lack of large prospective studies informed the rationale for our international observational study. We investigated delays in hospital admission as a surrogate for accessing timely fracture care and explored factors associated with delayed hospital admission.
Methods: In this prospective observational substudy of the ongoing International Orthopaedic Multicenter Study in Fracture Care (INORMUS), we enrolled patients with fracture across 49 hospitals in 18 low-income and middle-income countries, categorised into the regions of China, Africa, India, south and east Asia, and Latin America. Eligible patients were aged 18 years or older and had been admitted to a hospital within 3 months of sustaining an orthopaedic trauma. We collected demographic injury data and time to hospital admission. Our primary outcome was the number of patients with open and closed fractures who were delayed in their admission to a treating hospital. Delays for patients with open fractures were defined as being more than 2 h from the time of injury (in accordance with the Lancet Commission on Global Surgery) and for those with closed fractures as being a delay of more than 24 h. Secondary outcomes were reasons for delay for all patients with either open or closed fractures who were delayed for more than 24 h. We did logistic regression analyses to identify risk factors of delays of more than 2 h in patients with open fractures and delays of more than 24 h in patients with closed fractures. Logistic regressions were adjusted for region, age, employment, urban living, health insurance, interfacility referral, method of transportation, number of fractures, mechanism of injury, and fracture location. We further calculated adjusted relative risk (RR) from adjusted odds ratios, adjusted for the same variables. This study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02150980, and is ongoing.
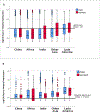
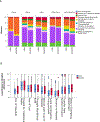
Findings: Between April 3, 2014, and May 10, 2019, we enrolled 31 255 patients with fractures, with a median age of 45 years (IQR 31-62), of whom 19 937 (63·8%) were men, and 14 524 (46·5%) had lower limb fractures, making them the most common fractures. Of 5256 patients with open fractures, 3778 (71·9%) were not admitted to hospital within 2 h. Of 25 999 patients with closed fractures, 7141 (27·5%) were delayed by more than 24 h. Of all regions, Latin America had the greatest proportions of patients with delays (173 [88·7%] of 195 patients with open fractures; 426 [44·7%] of 952 with closed fractures). Among patients delayed by more than 24 h, the most common reason for delays were interfacility referrals (3755 [47·7%] of 7875) and Third Delays (cumulatively interfacility referral and delay in emergency department: 3974 [50·5%]), while Second Delays (delays in reaching care) were the least common (423 [5·4%]). Compared with other methods of transportation (eg, walking, rickshaw), ambulances led to delay in transporting patients with open fractures to a treating hospital (adjusted RR 0·66, 99% CI 0·46-0·93). Compared with patients with closed lower limb fractures, patients with closed spine (adjusted RR 2·47, 99% CI 2·17-2·81) and pelvic (1·35, 1·10-1·66) fractures were most likely to have delays of more than 24 h before admission to hospital.
Interpretation: In low-income and middle-income countries, timely hospital admission remains largely inaccessible, especially among patients with open fractures. Reducing hospital-based delays in receiving care, and, in particular, improving interfacility referral systems are the most substantial tools for reducing delays in admissions to hospital.
Funding: National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, McMaster Surgical Associates, and Hamilton Health Sciences.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Interfacility transfer: an indicator of delay in fracture care.Lancet Glob Health. 2020 May;8(5):e623-e624. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30088-7. Lancet Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32353303 No abstract available.
-
Delays in hospital admissions for patients with fractures - Authors' reply.Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Aug;8(8):e1000. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30305-3. Lancet Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32710856 No abstract available.
-
Delays in hospital admissions for patients with fractures.Lancet Glob Health. 2020 Aug;8(8):e999. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30280-1. Lancet Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32710878 No abstract available.
References
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012; 380: 2197–223. - PubMed
-
- Meara JG, Leather AJM, Hagander L, et al. Global Surgery 2030: evidence and solutions for achieving health, welfare, and economic development. Lancet 2015; 386: 569–624. - PubMed
-
- Mock CN, Jurkovich GJ, nii-Amon-Kotei D, Arreola-Risa C, Maier RV. Trauma mortality patterns in three nations at different economic levels: implications for global trauma system development. J Trauma 1998; 44: 804–12; discussion 812–4. - PubMed
-
- Hsia R, Thind A, Mock CN, Hicks ER, Zakariah A, Mabweijano J. Prehospital and Emergency Care. In: Disease Control Priorities, Third Edition (Volume 1): Essential Surgery. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank, 2016: 245–62.

