COVID-19: Immunology and treatment options
- PMID: 32353634
- PMCID: PMC7185015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108448
COVID-19: Immunology and treatment options
Abstract
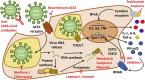
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV2 causes COVID-19, a pandemic threatening millions. As protective immunity does not exist in humans and the virus is capable of escaping innate immune responses, it can proliferate, unhindered, in primarily infected tissues. Subsequent cell death results in the release of virus particles and intracellular components to the extracellular space, which result in immune cell recruitment, the generation of immune complexes and associated damage. Infection of monocytes/macrophages and/or recruitment of uninfected immune cells can result in massive inflammatory responses later in the disease. Uncontrolled production of pro-inflammatory mediators contributes to ARDS and cytokine storm syndrome. Antiviral agents and immune modulating treatments are currently being trialled. Understanding immune evasion strategies of SARS-CoV2 and the resulting delayed massive immune response will result in the identification of biomarkers that predict outcomes as well as phenotype and disease stage specific treatments that will likely include both antiviral and immune modulating agents.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
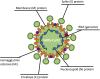
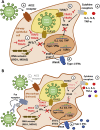
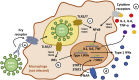
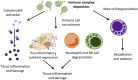
Comment in
-
Intestinal microbiome transfer, a novel therapeutic strategy for COVID-19 induced hyperinflammation?: In reply to, 'COVID-19: Immunology and treatment options', Felsenstein, Herbert McNamara et al. 2020'.Clin Immunol. 2020 Sep;218:108542. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108542. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32663514 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
mTORC inhibitor Sirolimus deprograms monocytes in "cytokine storm" in SARS-CoV2 secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis- like syndrome.Clin Immunol. 2020 Sep;218:108539. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108539. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32673711 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Drosten C., Gunther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.R., Becker S. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348(20):1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Zaki A.M., van Boheemen S., Bestebroer T.M., Osterhaus A.D., Fouchier R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367(19):1814–1820. - PubMed
-
- Hamre D., Procknow J.J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966;121(1):190–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

