Modulation of mTORC1 Signaling Pathway by HIV-1
- PMID: 32354054
- PMCID: PMC7291251
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9051090
Modulation of mTORC1 Signaling Pathway by HIV-1
Abstract
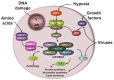
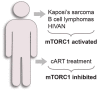
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) is a master regulator of cellular proliferation and survival which controls cellular response to different stresses, including viral infection. HIV-1 interferes with the mTORC1 pathway at every stage of infection. At the same time, the host cells rely on the mTORC1 pathway and autophagy to fight against virus replication and transmission. In this review, we will provide the most up-to-date picture of the role of the mTORC1 pathway in the HIV-1 life cycle, latency and HIV-related diseases. We will also provide an overview of recent trends in the targeting of the mTORC1 pathway as a promising strategy for HIV-1 eradication.
Keywords: HIV-1; HIV-1 related diseases; autophagy; mTORC1 pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mehrbod P., Ande S.R., Alizadeh J., Rahimizadeh S., Shariati A., Malek H., Hashemi M., Glover K.K.M., Sher A.A., Coombs K.M., et al. The roles of apoptosis, autophagy and unfolded protein response in arbovirus, influenza virus, and HIV infections. Virulence. 2019;10:376–413. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1605803. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Votteler J., Schubert U. Encyclopedia of Virology. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2008. Human Immunodeficiency Viruses: Molecular Biology; pp. 517–525.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

