COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 32354637
- PMCID: PMC7142878
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.03.018
COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
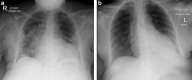
By 21 March 2020 infections related to the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 had affected people from 177 countries and caused 11,252 reported deaths worldwide. Little is known about risk, presentation and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection in kidney transplantation recipients, who may be at high-risk due to long-term immunosuppression, comorbidity and residual chronic kidney disease. Whilst COVID-19 is predominantly a respiratory disease, in severe cases it can cause kidney and multi-organ failure. It is unknown if immunocompromised hosts are at higher risk of more severe systemic disease. Therefore, we report on seven cases of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients (median age 54 (range 45-69), three females, from a cohort of 2082 managed transplant follow-up patients) over a six-week period in three south London hospitals. Two of seven patients presented within three months of transplantation. Overall, two were managed on an out-patient basis, but the remaining five required hospital admission, four in intensive care units. All patients displayed respiratory symptoms and fever. Other common clinical features included hypoxia, chest crepitation, lymphopenia and high C-reactive protein. Very high D dimer, ferritin and troponin levels occurred in severe cases and likely prognostic. Immunosuppression was modified in six of seven patients. Three patients with severe disease were diabetic. During a three week follow up one patient recovered, and one patient died. Thus, our findings suggest COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant patients may be severe, requiring intensive care admission. The symptoms are predominantly respiratory and associated with fever. Most patients had their immunosuppression reduced and were treated with supportive therapy.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 infection; immunosuppression; kidney transplantation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Early experience with COVID-19 in kidney transplantation.Kidney Int. 2020 Jun;97(6):1074-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32354635 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cyclosporine as a preferred calcineurin inhibitor in renal allograft recipients with COVID-19 infection.Kidney Int. 2020 Aug;98(2):507-508. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.024. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32505466 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Kidney transplantation trends in South Korea during the COVID-19 pandemic.Kidney Int. 2020 Aug;98(2):512-513. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.044. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32569651 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Kidney transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic: Potential long-term consequences of an early post-transplant infection.Transpl Infect Dis. 2021 Aug;23(4):e13446. doi: 10.1111/tid.13446. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Transpl Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32790932 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University of Medicine—Coronavirus Resource Center Coronavirus COVID-19 global cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. March 27, 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html Available at:
-
- UK Government. Number of coronavirus (COVID-19) cases and risk in the UK 2020. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-track-coronavirus-cases. Accessed April 14, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous