Giant prostatic hyperplasia and its causes
- PMID: 32355462
- PMCID: PMC7180407
- DOI: 10.6001/actamedica.v26i4.4209
Giant prostatic hyperplasia and its causes
Abstract
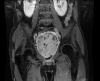
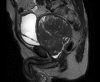
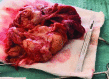
We present a case of a 59-year-old male who was admitted to the emergency department with urinary retention, with a history of lower urinary tract symptoms, with the value of serum prostate specific antigen level of 100 ng/mL and an estimated prostate size of 800 mL, according to magnetic resonance imaging. A prostate biopsy showed benign prostatic hyperplasia. Transvesical prostatectomy was performed, following additional procedure of transurethral resection of the prostate. To the best of our knowledge, this is the fourth highest prostate volume reported in medical literature. In this paper, we examine the factors that may have influenced the development of giant prostate hyperplasia.
Santrauka Straipsnyje pateikiamas 59 metų amžiaus vyro klinikinis atvejis. Pacientas, kurį ilgą laiką vargino apatinių šlapimo takų problemos, atvyko į skubios pagalbos skyrių dėl ūminio šlapimo susilaikymo. Prostatos specifinio antigeno koncentracija buvo 100 ng/ml, o magnetiniu rezonansu išmatuotos prostatos tūris siekė 800 ml. Atlikus prostatos biopsiją gautas atsakymas – gėrybinė prostatos hiperplazija. Pacientui atlikta suprapubinė prostatektomija, o vėliau transuretrinė prostatos rezekcija. Kiek yra žinoma, tai buvo ketvirta didžiausia prostata, aprašyta medicininėje literatūroje.Straipsnyje analizuojami veiksniai, kurie galėjo lemti milžiniškos prostatos atsiradimą.Raktažodžiai: gerybinė prostatos hiperplazija, gigantinė prostatos hiperplazija, prostata, transversinė prostatektomija.
Keywords: benign prostatic hyperplasia; giant prostatic hyperplasia; prostate; transvesical prostatectomy.
© Lietuvos mokslų akademija, 2020.
Figures

References
-
- Berry SJ Coffey DS Walsh PC Ewing LL. . The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984; 132: 474–9. - PubMed
-
- Erdemir F Harbin A Hellstrom WJG. . 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and erectile dysfunction: the connection. J Sex Med. 2008; 5: 2917–24. - PubMed
-
- Management of clinically localized prostate cancer. PubMed – NCBI [Internet]. [cited 2019. September 9]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16985859.
-
- Fishman JR Merrill DC. . A case of giant prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 1993; 42: 336–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
