Risk factors of brain metastases as initial failure in completely resected stage IIIA(N2) non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 32355818
- PMCID: PMC7186613
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.72
Risk factors of brain metastases as initial failure in completely resected stage IIIA(N2) non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to identify the risk factors of brain metastases (BM) as the initial site of failure in patients with completely resected stage IIIA (N2) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: From January 2005 and June 2012, the clinical data of 357 patients with completely resected stage IIIA (N2) NSCLC were reviewed in this study. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to identify the incidence of BM as the initial site of failure and survival. To assess the risk factors of BM, the log-rank test and Cox regression were used for univariate analysis and multivariate analysis, separately.
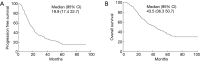
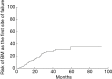
Result: Seventy-three (20.4%) patients developed BM; 60 patients had BM as their initial site of failure. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year risk for patients developing BM as the initial site of failure was 9.1%, 27.4% and 35.4%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed adenocarcinoma histology (P=0.000), number of regional LN >4 (P=0.018), multiple N2 stations (P=0.027), multiple region of LN involvement (P=0.010) were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing BM as the initial site of failure. Multivariate analysis showed adenocarcinoma (P=0.001; HR =0.150; 95% CI, 0.047-0.479), multiple regions of LN involvement (P=0.015; HR =2.010; 95% CI, 1.146-3.524) were significantly associated with the high risk of developing BM as the initial site of failure. In patients with adenocarcinoma and multiple regions of LN involvement, the 5-year actuarial risk of BM as the initial failure was 47.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: Adenocarcinoma and multiple regions of LN involvement were independent risk factors for BM as the initial failure in completely resected stage IIIA (N2) NSCLC. Prospective clinical trials are needed to verify the effect of PCI in the highest-risk subset we identified.
Keywords: Brain metastases (BM); adenocarcinoma and multiple region of LN involvement; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); risk factor.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
