Immunosuppressive strategies in lung transplantation
- PMID: 32355853
- PMCID: PMC7186623
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.117
Immunosuppressive strategies in lung transplantation
Abstract
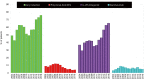
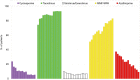
Lung transplantation is a viable option for those with end-stage lung disease which is evidenced by the continued increase in the number of lung transplantations worldwide. However, patients and clinicians are constantly faced with acute and chronic rejection, infectious complications, drug toxicities, and malignancies throughout the lifetime of the lung transplant recipient. Conventional maintenance immunosuppression therapy consisting of a calcineurin inhibitor (CNI), anti-metabolite, and corticosteroids have become the standard regimen but newer agents and modalities continue to be developed. Here we will review induction agents, maintenance immunosuppressives, adjunctive therapies and other strategies to improve long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Lung transplantation; induction; maintenance; review.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The series “Strategies to Achieve Long-Term Success of Lung Transplantation” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Goldfarb SB, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-fifth adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2018; Focus theme: Multiorgan Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018;37:1169-83. 10.1016/j.healun.2018.07.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Simulect® [package insert]. East Hanover, NJ: Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, 2018.
-
- Thymoglobulin® [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Genzyme Corporation, 2017.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
