An update on chronic lung allograft dysfunction
- PMID: 32355861
- PMCID: PMC7186740
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.05
An update on chronic lung allograft dysfunction
Abstract
Chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) remains a significant challenge and the major determinant of morbidity and mortality post lung transplantation (LTx). The definition of CLAD has evolved significantly over the last ten years, reflecting better understanding of pathophysiology and different phenotypes. While there is an agreed consensus approach to CLAD, questions remain regarding the limitations of lung function parameters as well as the role of imaging and histopathology. Here we present a current snapshot of the definition of CLAD, its evolution and future directions.
Keywords: Lung transplantation (LTx); chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD).
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The series “Strategies to Achieve Long-Term Success of Lung Transplantation” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

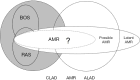
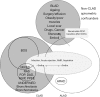
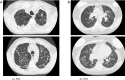
References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Golfarb SB, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-fifth Adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2018; Focus theme: Multiorgan Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018;37:1169-83. 10.1016/j.healun.2018.07.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cooper JD, Billingham M, Egan T, et al. A working formulation for the standardization of nomenclature and for clinical staging of chronic dysfunction in lung allografts. International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 1993;12:713-6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
