Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy versus EUS-FNA of pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32355885
- PMCID: PMC7164999
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1119-6543
Diagnostic yield of EUS-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy versus EUS-FNA of pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
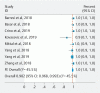
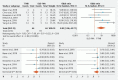
Background and study aims Accurate diagnosis and risk stratification of pancreatic cysts (PCs) is challenging. The aim of this study was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the feasibility, safety, and diagnostic yield of endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle biopsy (TTNB) versus fine-needle aspiration (FNA) in PCs. Methods Comprehensive search of databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane, Web of Science) for relevant studies on TTNB of PCs (from inception to June 2019). The primary outcome was to compare the pooled diagnostic yield and concordance rate with surgical pathology of TTNB histology and FNA cytology of PCs. The secondary outcome was to estimate the safety profile of TTNB. Results: Eight studies (426 patients) were included. The diagnostic yield was significantly higher with TTNB over FNA for a specific cyst type (OR: 9.4; 95 % CI: [5.7-15.4]; I 2 = 48) or a mucinous cyst (MC) (OR: 3.9; 95 % CI: [2.0-7.4], I 2 = 72 %). The concordance rate with surgical pathology was significantly higher with TTNB over FNA for a specific cyst type (OR: 13.5; 95 % CI: [3.5-52.3]; I 2 = 48), for a MC (OR: 8.9; 95 % [CI: 1.9-40.8]; I 2 = 29), and for MC histologic severity (OR: 10.4; 95 % CI: [2.9-36.9]; I 2 = 0). The pooled sensitivity and specificity of TTNB for MCs were 90.1 % (95 % CI: [78.4-97.6]; I 2 = 36.5 %) and 94 % (95 % CI: [81.5-99.7]; I 2 = 0), respectively. The pooled adverse event rate was 7.0 % (95 % CI: [2.3-14.1]; I 2 = 82.9). Conclusions TTNB is safe, has a high sensitivity and specificity for MCs and may be superior to FNA cytology in risk-stratifying MCs and providing a specific cyst diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Dr. Draganov is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Olympus, Cook Medical, Lumendi and Microtech. Dr. Yang is a consultant for US Endoscopy, Boston Scientific, Lumendi and Steris.
Figures
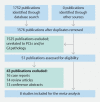





References
-
- Lee K S, Sekhar A, Rofsky N M et al.Prevalence of incidental pancreatic cysts in the adult population on MR imaging. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2079–2084. - PubMed
-
- Khashab M A, Kim K, Lennon A M et al.Should we do EUS/FNA on patients with pancreatic cysts? The incremental diagnostic yield of EUS over CT/RMI for prediction of cystic neoplasms. Pancreas. 2013;42:717–721. - PubMed
-
- Visser B C, Yeh B M, Qayyum A et al.Characterization of cystic pancreatic masses: relative accuracy of CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;189:648–656. - PubMed
-
- Brugge W R. The use of EUS to diagnose cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:S203–S209. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

