Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 32356609
- PMCID: PMC7193764
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002309.pub6
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is associated with cough, sputum production or dyspnoea, and a reduction in lung function, quality of life, and life expectancy. Apart from smoking cessation, no other treatments that slow lung function decline are available. Roflumilast and cilomilast are oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE₄) inhibitors proposed to reduce the airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction seen in COPD. This Cochrane Review was first published in 2011, and was updated in 2017 and 2020.
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of oral PDE₄ inhibitors for management of stable COPD.
Search methods: We identified randomised controlled trials (RCTs) from the Cochrane Airways Trials Register (date of last search 9 March 2020). We found other trials at web-based clinical trials registers.
Selection criteria: We included RCTs if they compared oral PDE₄ inhibitors with placebo in people with COPD. We allowed co-administration of standard COPD therapy.
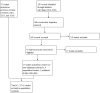
Data collection and analysis: We used standard Cochrane methods. Two independent review authors selected trials for inclusion, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias. We resolved discrepancies by involving a third review author. We assessed our confidence in the evidence by using GRADE recommendations. Primary outcomes were change in lung function (minimally important difference (MID) = 100 mL) and quality of life (scale 0 to 100; higher score indicates more limitations).
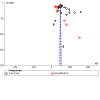
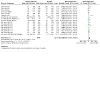
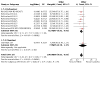
Main results: We found 42 RCTs that met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analyses for roflumilast (28 trials with 18,046 participants) or cilomilast (14 trials with 6457 participants) or tetomilast (1 trial with 84 participants), with a duration between six weeks and one year or longer. These trials included people across international study centres with moderate to very severe COPD (Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) grades II to IV), with mean age of 64 years. We judged risks of selection bias, performance bias, and attrition bias as low overall amongst the 39 published and unpublished trials. Lung function Treatment with a PDE₄ inhibitor was associated with a small, clinically insignificant improvement in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV₁) over a mean of 40 weeks compared with placebo (mean difference (MD) 49.33 mL, 95% confidence interval (CI) 44.17 to 54.49; participants = 20,815; studies = 29; moderate-certainty evidence). Forced vital capacity (FVC) and peak expiratory flow (PEF) were also improved over 40 weeks (FVC: MD 86.98 mL, 95% CI 74.65 to 99.31; participants = 22,108; studies = 17; high-certainty evidence; PEF: MD 6.54 L/min, 95% CI 3.95 to 9.13; participants = 4245; studies = 6; low-certainty evidence). Quality of life Trials reported improvements in quality of life over a mean of 33 weeks (St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) MD -1.06 units, 95% CI -1.68 to -0.43; participants = 7645 ; moderate-certainty evidence). Incidence of exacerbations Treatment with a PDE₄ inhibitor was associated with a reduced likelihood of COPD exacerbation over a mean of 40 weeks (odds ratio (OR) 0.78, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.84; participants = 20,382; studies = 27; high-certainty evidence), that is, for every 100 people treated with PDE₄ inhibitors, five more remained exacerbation-free during the study period compared with those given placebo (number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 20, 95% CI 16 to 27). No change in COPD-related symptoms nor in exercise tolerance was found. Adverse events More participants in the treatment groups experienced an adverse effect compared with control participants over a mean of 39 weeks (OR 1.30, 95% CI 1.22 to 1.38; participants = 21,310; studies = 30; low-certainty evidence). Participants experienced a range of gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, or dyspepsia. Diarrhoea was more commonly reported with PDE₄ inhibitor treatment (OR 3.20, 95% CI 2.74 to 3.50; participants = 20,623; studies = 29; high-certainty evidence), that is, for every 100 people treated with PDE₄ inhibitors, seven more suffered from diarrhoea during the study period compared with those given placebo (number needed to treat for an additional harmful outcome (NNTH) 15, 95% CI 13 to 17). The likelihood of psychiatric adverse events was higher with roflumilast 500 µg than with placebo (OR 2.13, 95% CI 1.79 to 2.54; participants = 11,168; studies = 15 (COPD pool data); moderate-certainty evidence). Roflumilast in particular was associated with weight loss during the trial period and with an increase in insomnia and depressive mood symptoms. Participants treated with PDE₄ inhibitors were more likely to withdraw from trial participation; on average, 14% in the treatment groups withdrew compared with 8% in the control groups. Mortality No effect on mortality was found (OR 0.98, 95% CI 0.77 to 1.24; participants = 19,786; studies = 27; moderate-certainty evidence), although mortality was a rare event during these trials.
Authors' conclusions: For this current update, five new studies from the 2020 search contributed to existing findings but made little impact on outcomes described in earlier versions of this review. PDE₄ inhibitors offered a small benefit over placebo in improving lung function and reducing the likelihood of exacerbations in people with COPD; however, they had little impact on quality of life or on symptoms. Gastrointestinal adverse effects and weight loss were common, and the likelihood of psychiatric symptoms was higher, with roflumilast 500 µg. The findings of this review provide cautious support for the use of PDE₄ inhibitors in COPD. In accordance with GOLD 2020 guidelines, they may have a place as add-on therapy for a subgroup of people with persistent symptoms or exacerbations despite optimal COPD management (e.g. people whose condition is not controlled by fixed-dose long-acting beta₂-agonist (LABA) and inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) combinations). More longer-term trials are needed to determine whether or not PDE₄ inhibitors modify FEV₁ decline, hospitalisation, or mortality in COPD.
Copyright © 2020 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Phillippa Poole: none known.
Sadia Janjua is funded full‐time as a systematic reviewer by a National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Programme Grant to complete work on this review.
Rebecca Fortescue is Co‐ordinating Editor for Cochrane Airways.
Figures













































Update of
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 19;9(9):CD002309. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002309.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 1;5:CD002309. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002309.pub6. PMID: 28922692 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Cilomilast 039 {published data only}
-
- 207499/039. A randomized, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cilomilast (15 mg twice daily) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (207499/039). gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/study/207499/039#rs (first received 28 September 2008).
-
- Edelson JD, Compton C, Nieman R, Robinson CB, Amit O, Bagchi I, et al. Cilomilast (Ariflo), a potent selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, reduces exacerbations in COPD patients: results of a 6 month trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2001;163(5 Suppl):A771.
-
- Edelson JD, Compton C, Nieman R, Robinson CB, Watt R, Amit O, et al. Cilomilast (Ariflo) improves health status in patients with COPD: results of a 6-month trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2001;163(5 Suppl):A277.
-
- Rennard SI, Schachter N, Strek M, Rickard K, Amit O. Cilomilast for COPD: results of a 6-month, placebo controlled study of a potent, selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4. Chest 2006;129(1):55-66. - PubMed
Cilomilast 042 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/042. A randomized, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cilomilast (15 mg twice daily) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/study/207499/042?search=study&search_t... (first received 28 September 2008).
Cilomilast 076 {published and unpublished data}
-
- 207499/076. A 12-week, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of SB207499 15 mg twice daily in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/files/pdf/24047.pdf (first received 28 September 2008).
-
- Gamble E, Grootendorst DC, Brightling CE, Troy S, Qiu Y, Zhu J, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor cilomilast (Ariflo) in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2003;168:976-82. - PubMed
Cilomilast 091 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/091. A randomized, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study followed by a 2-week, randomized, double-blind, run-out phase to evaluate the efficacy, safety, tolerability and discontinuation of SB207499 (15 mg twice daily) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/study/207499/091?search=study&search_t... (first received 28 September 2008).
Cilomilast 103657 {unpublished data only}
-
- CIL103657. GSK CTR-657. A randomized, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cilomilast (15 mg BID) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). gsk-studyregister.com/study?uniqueStudyId=CIL103657 (first received 24 August 2016).
Cilomilast 110 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/110. A 12-week, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of cilomilast 15 mg twice daily in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. gsk-studyregister.com/study/5979 (first received 11 December 2008).
Cilomilast 111 {published and unpublished data}
-
- 207499/111. A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to investigate the effect of cilomilast (15 mg twice daily) on trapped gas volume in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/files/pdf/24050.pdf (first received 28 September 2008).
-
- Zamel N, McClean P, Zhu J, Schryver B, Madan A, Robinson CB, et al. Effect of cilomilast (Ariflo) on trapped gas volume and indices of hyperinflation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A226.
Cilomilast 121 {unpublished data only}
-
- SB207499/121. A randomized, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cilomilast (15 mg BID) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. h/s3.amazonaws.com/ctr-gsk-7381/207499_121/430f519b-3d76-4244-9417-3bc8014... (first received 28 September 2008).
Cilomilast 156 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/156. A randomized, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of cilomilast (15 mg BID) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. s3.amazonaws.com/ctr-gsk-7381/207499_156/7dd49801-f278-4112-bbe8-f8ef3c6... (first received 20 May 2015).
Cilomilast 157 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/157. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of oral cilomilast (15 mg bd) when given as maintenance treatment for 12 months to subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. s3.amazonaws.com/ctr-gsk-7381/207499_157/37e6fc79-d3ca-46e1-b07a-c7c7995... (first received 28 September 2008).
Cilomilast 168 {published and unpublished data}
-
- 207499/168. A randomized, 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of cilomilast 15 mg twice daily in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/files/pdf/24054.pdf (first received 28 September 2008).
-
- Reisner C, Zhu J, Morris A, Lim J, Knobil K. Assessment of cardiac events via 24-hour electrocardiographic (Holter) monitoring with cilomilast in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. European Respiratory Journal 2003;22(Suppl 45):P522.
-
- Reisner C, Zhu J, Morris A, Lim J, Knobil K. Assessment of cardiac events via 24-hour electrocardiographic (Holter) monitoring with cilomilast in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In: American Thoracic Society 99th International Conference; 2003 May 16-21; Seattle. 2003.
Cilomilast 180 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/180. An 18-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study designed to compare treatment with cilomilast to that with placebo for changes in ventilatory mechanics and function (both at rest and during exercise), as well as related exertional dyspnea and exercise performance, in hyperinflated patients with stable COPD. s3.amazonaws.com/ctr-gsk-7381/207499_180/07613483-8e07-4a60-9f7c-fc67366... (first received 20 November 2008).
Cilomilast 181 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/181. A 13-week randomised, double-blind, parallel group, multicentre study to compare the bronchial anti-inflammatory activity of oral cilomilast (15 mg bd) with placebo twice daily in subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. s3.amazonaws.com/ctr-gsk-7381/207499_181/ac461889-1b68-44f0-a3ef-e3f7a9c... (first received 28 September 2008).
Compton 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Compton CH, Gubb J, Cedar E, Bakst A, Nieman RB, Amit O, et al. SB 207499, a second generation, oral PDE₄ inhibitor, improves health status in patients with COPD. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 1999 Oct 9-13; Madrid. 1999:P2237.
-
- Compton CH, Gubb J, Nieman R, Edelson J, Amit O, Bakst A, et al. Cilomilast, a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor for treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised, dose-ranging study. Lancet 2001;358(9278):265-70. - PubMed
COPD safety pool {published data only}
-
- Durmowicz AG. Cross discipline team leader review, application number 022522Orig1s000. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2011/022522Orig1s000CrossR.pdf (accessed prior to 14 February 2020).
Kavitha 2018 {published data only}
-
- Kavitha DM, Sarumathy S, Sasidharan SL, Shaik M, Sandeep G, Rajasekhar V, et al. A clinical study on safety and efficacy of formoterol and tiotropium combination compared to formoterol and tiotropium with roflumilast combination in treatment of moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 2018;11(3):184-6.
Liu 2018 {published data only}
NCT00874497 (EMPHASIS) {published data only}
-
- NCT00874497. Pilot study of tetomilast in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) associated with emphysema (EMPHASIS) [A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study to assess the pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of 50mg tetomilast administered as oral tablets in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associated with emphysema]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00874497 (first received 2 April 2009).
RO‐2455‐301‐RD (ACROSS) {published data only}
-
- NCT01313494. A chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) trial investigating roflumilast on safety and effectiveness in China, Hong Kong and Singapore. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01313494 2011.
-
- Zheng J, Yang J, Zhou X, Zhao L, Hui F, Wang H, et al. Roflumilast for the treatment of COPD in an Asian population: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study. Chest 2014;145(1):44-52. [CENTRAL: 978808] [EMBASE: 2014049205] [4900126000007427] [PMID: ] - PubMed
RO‐2455‐402‐RD (ROBERT) {published data only}
-
- 2011-000582-13. A 16-week, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, and parallel group trial to assess the anti-inflammatory effects of roflumilast in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The ROBERT study. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2011-000582-13/results (first received 4 January 2012).
-
- NCT01509677. Trial to assess the anti-inflammatory effects of roflumilast in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01509677 .
-
- Rabe KF, Hanauer G, Strigun A, Alagappan V. Effect of roflumilast on the serum metabolome of COPD patients. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2018;197:A7429.
-
- Rabe KF, Henrik W, Baraldo S, Pedersen F, Biondini D, Bagul N. Anti-inflammatory effects of roflumilast in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (ROBERT): a 16-week, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2018;6:827-36. - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Saetta M, Watz H, Baraldo S, Hanauer G, Göhring U-M, et al. Reduction in airway eosinophils in patients with COPD treated with roflumilast for 16 weeks: a double-blind, parallel-group, randomised, placebo-controlled biopsy trial. American Journal for Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2017;195:A7569.
RO‐2455‐404‐RD (REACT) {published data only}
-
- Kiff C, Ruiz S, Varol N, Gibson D, Davies A, Purkayastha D. Cost-effectiveness of roflumilast as add-on to triple inhaled therapy versus triple inhaled therapy in patients with severe and very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associated with chronic bronchitis in the UK. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2018;13(5):2707-20. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martinez FJ, Calverley PMA, Goehring U-M, Brose M, Fabbri LM, Rabe KF. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbations in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease uncontrolled by combination therapy (REACT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015;385(9971):857-66. - PubMed
-
- NCT01329029. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbation rate in patients with COPD treated with fixed combinations of LABA and ICS. A 52-week, randomised double-blind trial with roflumilast 500 µg versus placebo. The REACT trial. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01329029 (first received 30 March 2011).
Roflumilast DAL‐MD‐01 {published data only}
-
- Wells JM, Jackson PL, Viera L, Bhatt SP, Gautney J, Handley G, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of roflumilast. Effect on proline-glycine-proline and neutrophilic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2015;192(8):934-42. [CENTRAL: 1077156] [EMBASE: 2015481225] [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wells JM, Viera L, Gautney J, Handley GH, Jackson PL, Bhatt SP, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of roflumilast on markers of inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2015;191(Meeting Abstracts):A3643. [EMBASE: 72051470] - PMC - PubMed
Roflumilast FK1 101 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bredenbroker D, Syed J, Leichtl S, Rathgeb F, Wurst W. Roflumilast, a new, orally active phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is effective in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2002 14-18 Sep; Stockholm. 2002.
-
- Bredenbroker D, Syed J, Leichtl S, Rathgeb F, Wurst W. Safety of once-daily roflumilast, a new, orally active, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with COPD. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A595.
-
- Leichtl S, Syed J, Bredenbröker D, Rathgeb F, Wurst W. Efficacy of once-daily roflumilast, a new, orally active, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A229.
-
- Leichtl S, Syed J, Bredenbroker D, Rathgeb F, Wurst W. Roflumilast, a new, orally active, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is safe and well tolerated in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2002 Sep 14-17; Stockholm. 2002.
Roflumilast FK1 103 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Boszormenyi-Nagy G, Pieters WR, Steffen H, Timar M, Vinkler I, Teichmann P, et al. The effect of roflumilast treatment and subsequent withdrawal in patients with COPD. In: American Thoracic Society International Conference; 2005 May 20-25; San Diego. 2005.
-
- Rabe K, Similowski T, Bredenbröker D, Teichmann P, Böszörményi-Nagy G. Onset of action and effect of withdrawal of roflumilast in COPD. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2011 Sep 24-28; Amsterdam. 2011.
Roflumilast FLUI‐2011‐77 {published data only}
-
- De Backer J, Vos W, Claes R, Hufkens A, Bedert L, De Backer W. A double blind placebo controlled study to assess the effect of roflumilast in addition to LABA/LAMA/ICS treatment in COPD patients using novel biomarkers. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2014;189:A3773. [CENTRAL: 1035550]
-
- De Backer J, Vos W, Van Holsbeke C, Claes R, Hufkens A, Verplancke V, et al. A double blind placebo controlled study to assess the effect of roflumilast in addition to LABA/LAMA/ICS treatment in COPD patients using novel biomarkers. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2014;44(Suppl 58):4670. [CENTRAL: 1053499] [EMBASE: 72043284]
-
- De Backer W, Vos W, Van Holsbeke C, Vinchurkar S, Claes R, Hufkens A, et al. The effect of roflumilast in addition to LABA/LAMA/ICS treatment in COPD patients. European Respiratory Journal 2014;44(2):527-9. [CENTRAL: 998328] [EMBASE: 2014530222] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Roflumilast IN‐108 {unpublished data only}
-
- Brown P. Clinical pharmacology and biopharmaceutics review(s). Application number 022522Orig1s000. accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2011/022522Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf (accessed 9 October 2019).
Roflumilast JP‐706 {unpublished data only}
-
- Brown P. Clinical pharmacology and biopharmaceutics review(s). Application number 022522Orig1s000. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2011/022522Orig1s000ClinPharm... (accessed 9 October 2019).
Roflumilast M2‐107 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bateman ED, Holmes M, Muir JF, Andrae K, Witte S, Bredenbroeker D. Safety profile of roflumilast, a novel, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with moderate to severe COPD. In: American Thoracic Society 100th International Conference; 2004 May 21-26; Orlando. 2004.
-
- O'Donnell D, Muir JF, Jenkins C, Plit P, Brockhaus F, Witte S, et al. Roflumilast, a novel selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, improves quality of life and lowers exacerbation rate in patients with moderate to severe COPD [Abstract]. In: American Thoracic Society 100th International Conference; 2004 May 21-26; Orlando. 2004 Orlando.
-
- Rabe F, O'Donnell D, Muir F, Jenkins C, Witte S, Bredenbroeker D, et al. Roflumilast an oral once daily PDE4 inhibitor improves lung function and reduces exacerbation rates in patients with COPD. European Respiratory Journal 2004;24(Suppl 48):21s.
-
- Rabe KF, Bateman ED, O'Donnell D, Witte S, Bredenbröker D, Bethke TD. Roflumilast - an oral anti-inflammatory treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005;36(9485):563-71. - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Chapman KR, Joubert J, Vetter N, Witte S, Bredenboecker D. Roflumilast, a novel, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, improves lung function in patients with moderate to severe COPD. In: American Thoracic Society 100th International Conference; 2004 May 21-26; Orlando. 2004.
Roflumilast M2‐110 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00062582. Effect of roflumilast on pulmonary function and respiratory symptoms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (BY217/M2-110) [A 24 week, placebo-controlled, randomized, parallel group study comparing roflumilast 500 mcg daily vs placebo on pulmonary function and respiratory symptoms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00062582 (accessed prior to 23 June 2017).
Roflumilast M2‐111 {published data only}
-
- NCT00076089. OPUS study: effect of roflumilast on exacerbation rate in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (BY217/M2-111). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00076089 .
-
- Rennard SI, Calverley PM, Goehring UM, Bredenbroker D, Martinez FJ. Reduction of exacerbations by the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast - the importance of defining different subsets of patients with COPD. Respiratory Research 2011;12:18. [1465-993X: (Electronic). 1465-9921 (Linking)] [http://filehosting.pharmacm.com/DownloadService.ashx?client=CTR_MED_7111... ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rennard SI, Calverley PMA, Rempel A, Bredenbroker D, Martinez FJ. The effect of roflumilast treatment on exacerbations in patients with COPD results of a pooled analysis of two 1-year studies. In: American Thoracic Society International Conference; 2008 May 16-21; Toronto. 2008.
-
- Rusch H, Gooss A, Bethke TD, Rennard S. Efficacy of roflumilast when used with concomitant inhaled corticosteroids from the OPUS/RATIO studies. Respiration 2011;82(1):67-107.
Roflumilast M2‐111+M2‐112 {published data only}
-
- Rennard SI, Calverley PMA, Rempel A, Bredenbroker D, Martinez FJ. The effect of roflumilast treatment on exacerbations in patients with COPD results of a pooled analysis of two 1-year studies. In: American Thoracic Society International Conference; 2008 May 16-21; Toronto. 2008.
-
- Rusch H, Gooss A, Bethke TD, Rennard S. Efficacy of roflumilast when used with concomitant inhaled corticosteroids from the OPUS/RATIO studies. Respiration 2011;82(1):67-107.
Roflumilast M2‐112 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Calverley PM, Fabbri LM, Teichmann P, Bredenbroeker D. Effect of roflumilast on lung function and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: results of a one year study. Thorax 2005;2(Suppl II):ii42.
-
- Calverley PM, Sanchez-Toril F, McIvor A, Teichmann P, Bredenbroeker D, Fabbri LM. Effect of 1-year treatment with roflumilast in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2007;176(2):154-61. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PM, Sanchez-Toril F, McIvor RA, Teichmann P, Bredenbroeker D, Fabbri LM. Effect of roflumilast on lung function: a 1-year study in patients with severe to very severe COPD. In: Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society; 2006 May 19-24; San Diego. 2006.
-
- Fabbri LM, Sanchez-Toril F, McIvor RA, Teichmann P, Bredenbroeker D, Calverley PM. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbations: a 1-year study in patients with severe to very severe COPD. In: American Thoracic Society Conference; 2006 May 19-24; San Diego. 2006.
-
- Mclvor RA, Calverley PM, Sanchez-Toril F, Teichmann P, Bredenbroeker D, Fabbri LM. Effect of roflumilast on quality of life: a 1-year study in patients with severe to very severe COPD. In: American Thoracic Society Conference; 2006 May 19-24; San Diego. Vol. 3. 2006:A850.
Roflumilast M2‐118 {published data only}
-
- O'Donnell DE, Bredenbroker D, Brose M, Webb KA. Physiological effects of roflumilast at rest and during exercise in COPD. European Respiratory Journal 2012;39(5):1104-12. [ES:1399-3003: IL:0903-1936] - PubMed
Roflumilast M2‐119 {published data only}
-
- Hui D, Mahayiddin A, Roa C, Kwa KH, Bredenbröker D, Goehring UM, et al. Roflumilast in Asian patients with COPD: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2011 Sep 24-28; Amsterdam. 2011. - PubMed
-
- Lee SD, Hui DS, Mahayiddin AA, Roa CC, Kwa KH, Goehring UM, et al. Roflumilast in Asian patients with COPD: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Respirology 2011;16(8):1249-57. - PubMed
Roflumilast M2‐121 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00108823. The HERO-study: effects of roflumilast in patients with COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) (BY217/M2-121) [A 24-week, double blind, randomized study to investigate the effect of 500 µg roflumilast tablets once daily versus placebo on parameters indicative of hyperinflation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00108823 (first received 19 April 2005).
Roflumilast M2‐124 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Calverley PM, Rabe KF, Goehring U-M, Kristiansen S, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, et al. Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374(9691):685-94. - PubMed
-
- Martinez F, Hanania N, AURA Study Team. Efficacy and safety of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast in patients with symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the M2-124 study. Chest 2009;136(4):3S-e.
-
- NCT00297102. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbation rate in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): the AURA study (BY217/M2-124). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00297102 .
-
- Nowak D, Ehlken B, Kotchie R, Wecht S, Magnussen H. Roflumilast in combination with long-acting bronchodilators. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 2013;138(4):119-25. - PubMed
Roflumilast M2‐124+M2‐125 {published data only}
-
- Bateman ED, Rabe KF, Calverley PMA, Goehring UM, Brosee M, Bredenbroker D, et al. Roflumilast with long-acting beta2-agonists for COPD: influence of exacerbation history. European Respiratory Journal 2011;38(3):553-60. - PubMed
-
- Calverley P, Fabbri L, Rabe K, Goehring UM, Martinez F. Efficacy of the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in COPD patients with chronic bronchitis. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2009 Sep 12-16; Vienna. 2009.
-
- Calverley P, Martinez F, Goehring UM, Bredenbröker D, Brose M, Vogelmeier C. Impact of roflumilast treatment on the rate and duration of exacerbations and overall steroid load in patients with COPD. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2011 Sep 24-28; Amsterdam. 2011.
-
- Calverley PM, Rabe KF, Goehring U-M, Kristiansen S, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, et al. Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374(9691):685-94. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PMA, Rabe KF, Goehring UM, Kristiansen S, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ. Erratum: Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials (The Lancet (2009) 374 (685-694)). Lancet 2010;376(9747):1146. - PubMed
Roflumilast M2‐125 {published data only}
-
- Andrew M, Fernando J, HERMES Study Team. Efficacy and safety of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast in patients with symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the M2-125 study. Chest 2009;136(4):93S-94.
-
- Calverley PM, Rabe KF, Goehring U-M, Kristiansen S, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, et al. Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374(9691):685-94. - PubMed
-
- Nowak D, Ehlken B, Kotchie R, Wecht S, Magnussen H. Roflumilast in combination with long-acting bronchodilators. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 2013;138(4):119-25. - PubMed
Roflumilast M2‐127 {published data only}
-
- Chapman KR, McIvor A, Maltais F, EOS Study Team. Additional clinical benefit in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with roflumilast and salmeterol. Chest 2009;136(4):3S-f.
-
- Chapman KR, Rabe KF. Efficacy and safety of roflumilast in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) concomitantly treated with tiotropium or salmeterol. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2010;19(2):A12 [44].
-
- Fabbri LM, Calverley PM, Izquierdo-Alonso JL, Bundschuh DS, Brose M, Martinez FJ, et al. Roflumilast in moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with long acting bronchodilators: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374(9691):695-703. - PubMed
-
- Izquierdo JL, MacNee W, Biermann E, Goehring U-M, McIvor A. The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast provides additional clinical benefit in COPD patients receiving salmeterol. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2009 Sep 12-16; Vienna. 2009.
-
- Martinez F, McIvor A, Brose M, Larsson T, Goehring UM. Benefit of roflumilast therapy added to salmeterol in patients with varying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severity. Chest 2010;138(4):467A.
Roflumilast M2‐128 {published data only}
-
- Chapman KR, Rabe KF. Efficacy and safety of roflumilast in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) concomitantly treated with tiotropium or salmeterol. Primary Care Respiratory Journal 2010;19(2):A12 [44].
-
- Fabbri LM, Calverley PM, Izquierdo-Alonso JL, Bundschuh DS, Brose M, Martinez FJ, et al. Roflumilast in moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with long acting bronchodilators: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374(9691):695-703. - PubMed
-
- Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ, Goehring U-M, Brose M, Lakkis H, Rowe P. Roflumilast treatment with concomitant tiotropium: effect on lung function in severe COPD patients. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2012;27:S303. [CENTRAL: 980891] [EMBASE: 71296919]
-
- Paggiaro P, Foden A. Improvements in breathlessness in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with roflumilast and tiotropium. Chest 2009;136(4):3S-g, 4.
-
- Rabe K, Paggiaro P, Bernabeu L, Brose M, Geohring U-M, Fabbri L. Roflumilast, a PDE4 inhibitor, improves lung function in patients with COPD treated with tiotropium. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress; 2009 Sep 12-16; Vienna. 2009.
Roflumilast ROF‐MD‐07(RE2SPOND) {published data only}
-
- Ferguson GT, Rennard SI, Hanania NA, Zhu H, Siddiqui S, Sacks H. Roflumilast treatment in COPD patients taking a fixed-dose combination of long-acting β2 agonist (LABA) and inhaled corticosteroid (ICS): rationale and design of a prospective randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2012;185(Meeting Abstracts):A2946.
-
- Martinez FJ, Calverley PMA, Goehring U-M, Hodge R, Fabbri LM, Rabe KF. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbations in patients with severe COPD and a prior history of hospitalization taking combination therapy. European Respiratory Journal 2015;46:OA482.
-
- Martinez FJ, Rabe KF, Sethi S, Pizzichini E, McIvor A, Anzueto A, et al. Effect of roflumilast and inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting beta2-agonist on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations (RE(2)SPOND). A randomized clinical trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2016;194(5):559-67. [PMID: ] - PubMed
-
- PER-114-11. A 52-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate the effect of roflumilast 500 µg on exacerbation rate in subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) treated with a fixed-dose combination of long-acting beta agonist and inhaled corticosteroid (LABA/ICS). www.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=PER-114-11 .
-
- Rennard SI, Martinez FJ, Rabe KF, Sethi S, Pizzichini E, McIvor A, et al. Effect of roflumilast in COPD patients receiving inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting beta2-agonist fixed-dose combination: RE2SPOND rationale and study design. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2016;11(1):1921-8. [CENTRAL: 1180201] [EMBASE: 20160624756] [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Urban 2018 (ELASTIC) {published data only}
-
- Urban M, Kreibich N, Funk G-C, Burghuber OC. Effects of roflumilast on subclinical atherosclerosis in COPD - a randomised controlled trial [Effects of the anti-inflammatory drug "ROFLUMILAST" on markers of early atherosclerosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2011-004152-19/AT (first received 17 February 2012).
-
- Urban M, Kreibich N, Funk G-C, Burghuber OC. Effects of roflumilast on subclinical atherosclerosis in COPD - a randomised controlled trial. European Respiratory Journal 2017;50:PA693.
References to studies excluded from this review
Borker 2003 {published data only}
-
- Borker RD, Morris A, Lim J, Zhu J, Reisner C. Effect of cilomilast on quality of life improvement/deterioration and non-drug costs in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest 2003;124(4):170S-b,171.
CTRI/2012/09/002961 {published data only}
-
- CTRI/2012/09/002961. A randomized, open labelled, multi centric parallel group three arms clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of roflumilast 500mcg tablet in chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder. who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2012/09/002961 (first received 5 September 2012).
CTRI/2014/01/004370 {published data only}
-
- CTRI/2014/01/004370. A clinical trial study of oral Roflumilast 0.5mg Tablet and combination therapy of Roflumilast 0.5 mg tablet plus Salmeterol 25mcg oral inhaler and combination therapy of Roflumilast 0.5 mg tablet plus Tiotropium 9mcg oral inhaler in adult patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [An open-label, prospective, three arm, parallel group, randomized, multicentric phase-III clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety between monotherapy of oral Roflumilast 0.5mg Tablet and combination therapy of Roflumilast 0.5 mg tablet plus Salmeterol 25mcg oral inhaler and combination therapy of Roflumilast 0.5 mg tablet plus Tiotropium 9mcg oral inhaler in adult patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]. who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2014/01/004370 (first received 31 January 2014).
Ferguson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson G, Fischer TL, Morris A, Zhu J, Barnhart F, Reisner C. Cardiovascular safety of cilomilast in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest 2003;124(4):171S.
Fischer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Fischer T, Borker R, Barnhart F, Morris A, Zhu J. Effect of cilomilast on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with impaired quality of life. Chest 2003;124(4):129S.
Grootendorst 2001 {published data only}
-
- Grootendorst DC, Gauw SA, Kelly J, Murdoch RD, Sterk PJ, Rabe KF. First dose bronchodilating effect of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibition by cilomilast (Ariflo) with or without co-administration of salbutamol and/or ipratropium in COPD patients. European Respiratory Journal 2001;18(Suppl 33):1:35s.
Grootendorst 2002 {published data only}
-
- Grootendorst DC, Gauw SA, Verhoosel R, Van der Veen H, Van der Linden A, Moesker H, et al. Effect of a PDE4 inhibitor (Bay 19-8004) on FEV1 and airway inflammation in patients with COPD. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(8 Suppl):A226.
Grootendorst 2003 {published data only}
-
- Grootendorst DC, Gauw SA, Baan R, Kelly J, Murdoch RD, Sterk PJ, et al. Does a single dose of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, cilomilast (15mg), induce bronchodilation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Pulmonary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2003;16(2):115-20. - PubMed
Grootendorst 2007 {published data only}
GSK256066 {published data only}
-
- Lazaar AL, Mistry S, Barrett C, Lulic-Burns Z. A four-week randomized study of the safety and tolerability of the inhaled PDE4 inhibitor GSK256066 in COPD. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2010;181(Meeting Abstracts):A4444.
Kelsen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kelsen SG, Rennard SI, Chodosh S, Schryver B, Vleisides C, Zhu J. COPD exacerbation in a 6-month trial of cilomilast (Ariflo), a potent, selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A271.
Knobil 2003 {published data only}
-
- Knobil K, Morris A, Zhu J, Fischer T, Reisner C. Cilomilast is efficacious in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In: American Thoracic Society 99th International Conference; 2003 May 16-21; Seattle. 2003:A035; Poster D92.
-
- Reisner C, Morris A, Zhu J, Fischer T, Knobil K. Cilomilast is efficacious in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. European Respiratory Journal 2003;22(Suppl 45):P530.
Lim 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lim S, Zhu J, Lake P. Cilomilast decreases exacerbations and maintains lung function in patients with poorly reversible COPD. European Respiratory Journal 2004;24(Suppl 48):88s.
NCT00246935 {published data only}
-
- NCT00246935. Long-term study of safety and efficacy of roflumilast in Japanese patients older than 40 years with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (APTA-2217-08) [A long-term study of APTA-2217 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/nct00246935 (first received 1 November 2005).
NCT01849341 {published data only}
-
- NCT01849341. Roflumilast safety administered once a day on alternate days for two weeks compared to the usual dosage once daily [Clinical trial phase III blind, parallel group to analyze differences in the safety of roflumilast administered once a day on alternate days for two weeks compared to the usual dosage once daily]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01849341 (first received 8 May 2013).
NCT01973998 {published data only}
-
- NCT01973998. Effects of roflumilast in hospitalized chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) on mortality and re-hospitalization. clinicaltrials.gov/show/nct01973998 (first received 1 November 2013).
NCT02018432 {published data only}
-
- NCT02018432. Strategy to improve adherence of roflumilast [Adherence to therapy in COPD patients under dose escalation of roflumilast]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/nct02018432 (first received 23 December 2013).
Nieman 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Nieman RB, Taneja DT, Amit O, Benincosa LJ, Compton CH, Bethala VK, et al. The effects of low dose SB207499, a second generation, oral PDE4 inhibitor, in patients with COPD. In: European Respiratory Society Congress; 1999 Oct 9-13; Madrid. 1999.
Pascoe 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Pascoe SJ, Bonner J, Hauffe S, Bohnemeier H. Gradual dose escalation of QAK423, a novel PDE4 inhibitor, significantly improves the tolerability. In: American Thoracic Society International Conference; 2007 May 18-23; San Francisco. 2007.
Rabe 2017 {published data only}
-
- Rabe KF, Calverley PMA, Martinez FJ, Fabbri LM. Effect of roflumilast in patients with severe COPD and a history of hospitalisation. European Respiratory Journal 2017;50(1):1700158. - PubMed
Reisner 2003 {published data only}
-
- Reisner C, Morris A, Barnhart F, Fischer TL, Acusta A, Darken P. Cilomilast reduces exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest 2003;124:4.
Rennard 2008 {published data only}
-
- Rennard S, Knobil K, Rabe KF, Morris A, Schachter N, Locantore N, et al. The efficacy and safety of cilomilast in COPD. Drugs 2008;68(Suppl 2):3-57. - PubMed
Roflumilast JP708 {unpublished data only}
-
- Brown P. Center for drug evaluation and research application number: 022522Orig1s000. Pharmacology review. www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2011/022522Orig1s000PharmR.pdf (accessed prior to 28 June 2017).
Sadigov 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sadigov A, Akhundov S, Bagirov R. Analysis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations with the triple therapy compared with dual and single bronchodilator therapy: which treatment is better for patients with severe disease? Chest 2014;145(3):425A. [CENTRAL: 991341] [EMBASE: 71429002]
-
- Sadigov AS, Bagirov R, Abbasov C. Analysis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations with the triple therapy compared with dual treatment: is it better treatment tool for patients with severe disease? American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2014;189:A3770. [CENTRAL: 1035664] [EMBASE: 72043281]
Sadigov 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sadigov A, Huseynova S. Efficacy and safety of dual anti-inflammatory combination of fluticasone and roflumilast for the treatment of COPD: is dual better than single? American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2015;191(Meeting Abstracts):A3968. [CENTRAL: 1101148] [EMBASE: 72051845]
SB207499/040 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/040. A multicentre, open-label extension study to evaluate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of oral SB-207499 (15 mg twice daily) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. www.gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/files/pdf/24044.pdf (first received 28 September 2008).
SB207499/041 {unpublished data only}
-
- 207499/041. A multicenter open-label extension study to evaluate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of oral cilomilast (15 mg twice daily) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. www.gsk-clinicalstudyregister.com/files/pdf/24045.pdf (first received 28 September 2008).
Song 2005 {published data only}
-
- Song Y, Wang C, Liao X, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhao Z, et al. Improvement in lung residual volume in patients with COPD roles of anti-inflammation activity of cilomilast. Respiratory 2005;10(Suppl 3):A135.
Spencer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Spencer MD, Zhu J, Izard D. The direct costs of exacerbations in COPD and the effect of cilomilast treatment. European Respiratory Journal 2002;20(Suppl 38):245s.
Vestbo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Vestbo J, Tan L, Atkinson G. A 6 week study of the efficacy and safety of UK 500,001 dry powder for inhalation (DPI) in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. European Respiratory Journal 2007;30(Suppl 51):612s [P3598].
Vestbo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Vestbo J, Tan L, Atkinson G, Ward J. A controlled trial of 6-weeks' treatment with a novel inhaled phosphodiesterase type-4 inhibitor in COPD. European Respiratory Journal 2009;33(5):1039-44. - PubMed
Wang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wang C, Song Y, Liao X. Efficacy and anti-inflammation activity of a selective phospodiesterase-4 inhibitor cilomilast in treatment of COPD. Chest 2005;128(4):262S-a.
Watz 2013 {published data only}
-
- Watz H, Mistry SJ, Lazaar AL, IPC101939 investigators. Safety and tolerability of the inhaled phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor GSK256066 in moderate COPD. Pulmonary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2013;26(5):588-95. [CENTRAL: 872117] [EMBASE: 2013527752] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Watz 2016 {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2013-001788-21-SK. Study to evaluate how to optimise the use of roflumilast in subjects who have a lung disease called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [A multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase 3 study to evaluate tolerability and pharmacokinetics of 500 µg roflumilast once daily with an up-titration regimen in COPD, including an open-label down-titration period evaluating tolerability and pharmacokinetics of 250 µg roflumilast once daily in subjects not tolerating 500 µg roflumilast once-daily]. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2013-001788-21/results (first received 6 February 2014).
-
- Facius A, Bagul N, Gardiner P, Watz H. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a 4-week up-titration regimen of roflumilast in the optimize study OS. Pneumologie 2018;72(Suppl 1):S92.
-
- Facius, Bagul N, Gardiner P, Watz H. Pharmacokinetics of a 4-week up-titration regimen of roflumilast in the optimize study. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2017;195:A1337.
-
- NCT02165826. Evaluation of tolerability and pharmacokinetics of roflumilast, 250μg and 500μg, as add-on to standard COPD treatment to treat severe COPD (OPTIMIZE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02165826 (first received 18 June 2014).
-
- Watz H, Bagul N, Nip K, Sun R, Goehring U-M, Calverley P, et al. Tolerability of different dosing regimens of roflumilast in severe COPD (OPTIMIZE). European Respiratory Journal 2016;48:PA308.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Barnes 2014 {published data only}
EUCTR2004‐004442‐40‐GB {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2004-004442-40-GB. 500µg roflumilast once daily in combination with 50µg salmeterol twice daily versus 50µg salmeterol twice daily alone over 52 weeks in patients with COPD. who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=EUCTR2004-004442-40-GB (first received 23 February 2005).
Mahmud 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mahmud AM, Hossain A, Hassan R, Khan AS, Bennoor KS, Shaheen M, et al. Placebo controlled study of roflumilast in Bangladeshi COPD patients. Respirology 2013;18(Suppl 4):125 [PS160]. [CENTRAL: 980913] [EMBASE: 71371785]
NCT00671073 {published data only}
-
- NCT00671073. Study to assess efficacy and safety of oglemilast in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00671073 (first received 2 May 2008).
NCT01595750 {published data only}
-
- NCT01595750. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effect of roflumilast on endothelial function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (REVASC) [Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effect of roflumilast on endothelial function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01595750 (first received 10 May 2012).
NCT01701934 {published data only}
-
- NCT01701934. Impact of roflumilast on visceral adiposity and metabolic profile in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (RAMBO). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01701934 (first received 5 October 2012).
References to ongoing studies
NCT02451540 2015 {published data only}
-
- 2015-000053-21. Placebo controlled study to assess the effect of Roflumilast in hyperinflated COPD patients in addition to LABA/LAMA therapy using functional respiratory imaging. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2015-000053-21/BE (first received 14 April 2015).
-
- NCT02451540. Evaluation of the effect of roflumilast in hyperinflated COPD patients using functional respiratory imaging [Placebo controlled study to assess the effect of roflumilast in hyperinflated COPD patients in addition to LABA/LAMA therapy using functional respiratory imaging]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02451540 (first received 7 May 2015).
NCT02671942 2016 {published data only}
-
- NCT02671942. A multicenter randomized double-blind clinical study evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics of roflumilast in COPD patients. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02671942 (first received 25 January 2016).
Additional references
Agusti 2005
-
- Agusti A. COPD, a multicomponent disease: implications for management. Respiratory Medicine 2005;99(6):670-82. - PubMed
Barnes 2000
-
- Barnes P. Medical progress: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;343:269-80. - PubMed
Barnes 2003
-
- Barnes P. Theophylline: new perspectives for an old drug. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2003;167(6):813-8. - PubMed
Barnes 2005
-
- Barnes P. Theophylline in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: new horizons. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 2005;2(4):334-9. - PubMed
Boswell‐Smith 2006
Calverley 2007
-
- Calverley PM, Anderson JA, Celli B, Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones PW, et al. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;356(8):775-89. - PubMed
Calverley 2009
-
- Calverley PM, Rabe KF, Goehring UM, Kristiansen S, Fabbri LM, Martinez FJ. Roflumilast in symptomatic chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374:685-94. - PubMed
Celli 2004
-
- Celli B, MacNee W. Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. European Respiratory Journal 2004;23(6):932-46. - PubMed
Cochrane Airways 2019
-
- Cochrane Airways Trials Register. airways.cochrane.org/trials-register (accessed 7 May 2019).
Donohue 2005
-
- Donohue J. Minimal clinically important differences in COPD lung function. COPD 2005;2:111-24. - PubMed
Essayan 2001
-
- Essayan D. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2001;108(5):671-80. - PubMed
Fabbri 2009
-
- Fabbri LM, Calverley PM, Izquierdo-Alonso JL, Bundschuh DS, Brose M, Martinez FJ, et al. Roflumilast in moderate-to-severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treated with long acting bronchodilators: two randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2009;374(9691):695-703. - PubMed
GOLD 2020
-
- From the global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD, global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease (GOLD) 2020. goldcopd.org (accessed 11 February 2020).
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 31 May 2017. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.Available at gradepro.org.
Guyatt 2008
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2019
-
- Higgins JT, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Sterne AC. Chapter 8. Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In: Higgins JT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane, 2019. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Jones 2005
-
- Jones P. St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire: MCID. COPD 2005;2:75-9. - PubMed
Le Rouzic 2018
-
- Le Rouzic O, Roche N, Cortot AB, Tillie-Leblond I, Masure F, Perez T et al. Defining the "frequent exacerbator" phenotype in COPD. Chest Journal 2018;153(5):1106-15. - PubMed
Luo 2016
Mathers 2005
-
- Mathers C, Loncar D. Updated projections of global mortality and burden of disease, 2002-2030: data sources, methods and results. Evidence and Information for Policy Working Paper. who.int/healthinfo/statistics/bod_projections2030_paper.pdf (accessed prior to 28 June 2017).
Moher 2009
Rennard 2014
-
- Rennard SI, Sun SX, Tourkodimitris S, Rowe P, Goehring UM, Bredenbröker D, et al. Roflumilast and dyspnea in patients with moderate to very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a pooled analysis of four clinical trials. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2014;9:657-73. - PMC - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Shen 2018
-
- Shen LF, Lv XD, Chen WY, Yang Q, Fang ZX, Lu WF. Effect of roflumilast on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Irish Journal of Medical Science 2018;187(3):731-8. - PubMed
TORCH 2007
-
- Calverley P, Anderson J, Celli B, Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones P, et al. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;356(8):775-89. - PubMed
Torphy 1998
-
- Torphy T. Phosphodiesterase isozymes: molecular targets for novel antiasthma agents. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1998;157(2):351-70. - PubMed
Torphy 1999
-
- Torphy T, Barnette M, Underwood D, Griswold DE, Christensen SB, Murdoch RD, et al. Ariflo (SB 207499), a second generation phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor for the treatment of asthma and COPD: from concept to clinic. Pulmonary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1999;12(2):131-5. - PubMed
Van Geffen 2015
-
- Van Geffen WH, Slebos DJ, Kerstjens HA. Hyperinflation in COPD exacerbations. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2015;12:e43-44. - PubMed
Vignola 2004
-
- Vignola A. PDE4 inhibitors in COPD - a more selective approach to treatment. Respiratory Medicine 2004;98(6):495-503. - PubMed
Wedzicha 2007
Wedzicha 2016
White 2003
White 2013
-
- White W, Cooke G, Kowey P, Calverley P, Bredenbröker D, Goehring U, et al. Cardiovascular safety in patients receiving roflumilast for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest 2013;144(3):758-65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

