The Early Detection Research Network: A National Infrastructure to Support the Discovery, Development, and Validation of Cancer Biomarkers
- PMID: 32357955
- PMCID: PMC11106613
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-0237
The Early Detection Research Network: A National Infrastructure to Support the Discovery, Development, and Validation of Cancer Biomarkers
Abstract
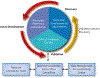
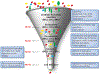
In 2000, the NCI (Rockville, MD) established the Early Detection Research Network (EDRN) to identify, develop, and validate biomarkers to improve the detection of early-stage cancers and risk assessment. This consortium of more than 300 investigators at academic institutions and in the private sector is working collaboratively to bring biomarkers and imaging methods to clinical fruition. Although significant roadblocks have hindered the field of biomarker discovery and validation, the EDRN has helped overcome many of them by setting well-defined strategies and milestones focused on solving defined unmet clinical needs. The EDRN has implemented measures to improve biomarker discovery and validation, such as data sharing, use of common data elements, generating multidisciplinary and multi-institutional collaborations within a cohesive and productive team environment, and putting emphasis on quality control and data replication for all candidate biomarkers for reaching a "go" or "no go" decision. A measure of the success of the EDRN is the number of biomarkers tests or devices approved by the FDA to which EDRN investigators have made significant contributions and the number of biomarkers tests developed by EDRN investigators that are available in Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments laboratories.See all articles in this CEBP Focus section, "NCI Early Detection Research Network: Making Cancer Detection Possible."
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Statement of Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Srivastava S, Kramer BS. Early detection cancer research network. Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology 2000;80(8):1147–8. - PubMed
-
- Gewin V Missing the mark. Nature 2007;449(7164):770–1. - PubMed
-
- Io Medicine, Council NR. Large-Scale Biomedical Science: Exploring Strategies for Future Research Nass SJ, Stillman BW, editors. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2003. 296 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

