Effective combinatorial immunotherapy for penile squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32358507
- PMCID: PMC7195486
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15980-9
Effective combinatorial immunotherapy for penile squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
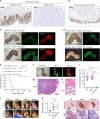
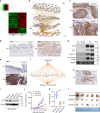
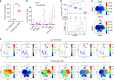
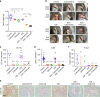
Penile squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) accounts for over 95% of penile malignancies and causes significant mortality and morbidity in developing countries. Molecular mechanisms and therapies of PSCC are understudied, owing to scarcity of laboratory models. Herein, we describe a genetically engineered mouse model of PSCC, by co-deletion of Smad4 and Apc in the androgen-responsive epithelium of the penis. Mouse PSCC fosters an immunosuppressive microenvironment with myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) as a dominant population. Preclinical trials in the model demonstrate synergistic efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade with the MDSC-diminishing drugs cabozantinib or celecoxib. A critical clinical problem of PSCC is chemoresistance to cisplatin, which is induced by Pten deficiency on the backdrop of Smad4/Apc co-deletion. Drug screen studies informed by targeted proteomics identify a few potential therapeutic strategies for PSCC. Our studies have established what we believe to be essential resources for studying PSCC biology and developing therapeutic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrándiz-Pulido C, de Torres I, García-Patos V. Penile squamous cell carcinoma. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr.áficas (Engl. Ed.) 2012;103:478–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

