Circulating biomarkers and cardiac function over 3 years after chemotherapy with anthracyclines: the ICOS-ONE trial
- PMID: 32358917
- PMCID: PMC7373944
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12695
Circulating biomarkers and cardiac function over 3 years after chemotherapy with anthracyclines: the ICOS-ONE trial
Abstract
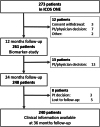
Aims: A multicentre trial, ICOS-ONE, showed increases above the upper limit of normality of cardiac troponin (cTn) in 27% of patients within 12 months after the end of cancer chemotherapy (CT) with anthracyclines, whether cardiac protection with enalapril was started at study entry in all (prevention arm) or only upon first occurrence on supra-normal cTn (troponin-triggered arm). The aims of the present post hoc analysis were (i) to assess whether anthracycline-based treatment could induce cardiotoxicity over 36 month follow-up and (ii) to describe the time course of three cardiovascular biomarkers (i.e. troponin I cTnI-Ultra, B-type natriuretic peptide BNP, and pentraxin 3 PTX3) and of left ventricular (LV) function up to 36 months.
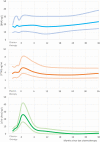
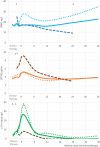
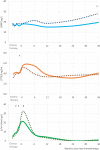
Methods and results: Eligible patients were those prescribed first-in-life CT, without evidence of cardiovascular disease, normal cTn, LV ejection fraction (EF) >50%, not on renin-angiotensin aldosterone system antagonists. Patients underwent echocardiography and blood sampling at 24 and 36 months. No differences were observed in biomarker concentration between the two study arms, 'prevention' vs. 'troponin-triggered'. During additional follow-up 13 more deaths occurred, leading to a total of 23 (9.5%), all due to a non-cardiovascular cause. No new occurrences of LV-dysfunction were reported. Two additional patients were admitted to the hospital for cardiovascular causes, both for acute pulmonary embolism. No first onset of raised cTnI-Ultra was reported in the extended follow-up. BNP remained within normal range: at 36 months was 23.4 ng/L, higher (N.S.) than at baseline, 17.6 ng/L. PTX3 peaked at 5.2 ng/mL 1 month after CT and returned to baseline values thereafter. cTnI-Ultra peaked at 26 ng/L 1 month after CT and returned to 3 ng/L until the last measurement at 36 months. All echocardiographic variables remained stable during follow-up with a median LVEF of 63% and left atrial volume index about 24 mL/m2 .
Conclusions: First-in-life CT with median cumulative dose of anthracyclines of 180 mg/m2 does not seem to cause clinically significant cardiac injury, as assessed by circulating biomarkers and echocardiography, in patients aged 51 years (median), without pre-existing cardiac disease. This may suggest either a 100% efficacy of enalapril (given as preventive or troponin-triggered) or a reassuringly low absolute cardiovascular risk in this cohort of patients, which may not require intensive cardiologic follow-up.
Keywords: Anthracyclines; Biomarkers; Cardiac dysfunction; Cardio-oncology; Echocardiography; Troponin.
© 2020 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G, Tedeschi I, Meroni CA, Veglia F, Civelli M, Lamantia G, Colombo N, Curigliano G, Fiorentini C, Cipolla CM. Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation 2015; 131: 1981–1988. - PubMed
-
- Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, Aboyans V, Asteggiano R, Galderisi M, Habib G, Lenihan DJ, Lip GYH, Lyon AR, Lopez Fernandez T, Mohty D, Piepoli MF, Tamargo J, Torbicki A, Suter TM, ESC Scientific Document Group . 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: The Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2768–2801. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Banchs J, Mousavi N, Plana JC, Scherrer‐Crosbie M, Thavendiranathan P, Barac A. Contemporary role of echocardiography for clinical decision making in patients during and after cancer therapy. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2018; 11: 1122–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

