Antiviral activities of type I interferons to SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 32360182
- PMCID: PMC7188648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104811
Antiviral activities of type I interferons to SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
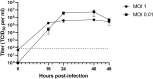
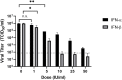
There is an urgent need to identify antivirals to curtail the COVID-19 pandemic. Herein, we report the sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 to recombinant human interferons α and β (IFNα/β). Treatment with IFN-α or IFN-β at a concentration of 50 international units (IU) per milliliter reduces viral titers by 3.4 log or over 4 log, respectively, in Vero cells. The EC50 of IFN-α and IFN-β treatment is 1.35 IU/ml and 0.76 IU/ml, respectively, in Vero cells. These results suggest that SARS-CoV-2 is more sensitive than many other human pathogenic viruses, including SARS-CoV. Overall, our results demonstrate the potential efficacy of human Type I IFN in suppressing SARS-CoV-2 infection, a finding which could inform future treatment options for COVID-19.
Keywords: Antiviral therapy; COVID-19; Innate immune; Interferon; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Update of
-
Potent Antiviral Activities of Type I Interferons to SARS-CoV-2 Infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Apr 5:2020.04.02.022764. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.02.022764. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Antiviral Res. 2020 Jul;179:104811. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104811. PMID: 32511327 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Dahl H., Linde A., Strannegard O. In vitro inhibition of SARS virus replication by human interferons. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2004;36:829–831. - PubMed
-
- Devaraj S.G., Wang N., Chen Z., Chen Z., Tseng M., Barretto N., Lin R., Peters C.J., Tseng C.T., Baker S.C., Li K. Regulation of IRF-3-dependent innate immunity by the papain-like protease domain of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:32208–32221. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

