Cytokine storm intervention in the early stages of COVID-19 pneumonia
- PMID: 32360420
- PMCID: PMC7182527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.04.002
Cytokine storm intervention in the early stages of COVID-19 pneumonia
Abstract
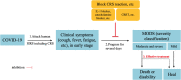
Clinical intervention in patients with corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has demonstrated a strong upregulation of cytokine production in patients who are critically ill with SARS-CoV2-induced pneumonia. In a retrospective study of 41 patients with COVID-19, most patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection developed mild symptoms, whereas some patients later developed aggravated disease symptoms, and eventually passed away because of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), as a consequence of a severe cytokine storm. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infected pneumonia were first published January 30th, 2020; these guidelines recommended for the first time that cytokine monitoring should be applied in severely ill patients to reduce pneumonia related mortality. The cytokine storm observed in COVID-19 illness is also an important component of mortality in other viral diseases, including SARS, MERS and influenza. In view of the severe morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 pneumonia, we review the current understanding of treatment of human coronavirus infections from the perspective of a dysregulated cytokine and immune response.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine storm; Inflammation; Lung damage; SARS-CoV2.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cytokine storm with rapidly elevated interleukin-6 indicates sudden death in patients with critical COVID-19.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Apr;58:30-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 32873506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tanaka T., Narazaki M., Kishimoto T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy. 2016;8(8):959–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous