Liu Shen capsule shows antiviral and anti-inflammatory abilities against novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 via suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 32360580
- PMCID: PMC7192119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104850
Liu Shen capsule shows antiviral and anti-inflammatory abilities against novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 via suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
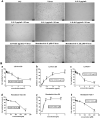
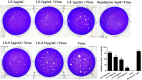
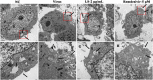
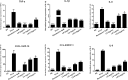
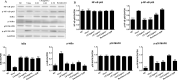
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has spread worldwide through person-to-person contact, causing a public health emergency of international concern. At present, there is no specific antiviral treatment recommended for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Liu Shen capsule (LS), a traditional Chinese medicine, has been proven to have a wide spectrum of pharmacological properties, such as anti-inflammatory, antiviral and immunomodulatory activities. However, little is known about the antiviral effect of LS against SARS-CoV-2. Herein, the study was designed to investigate the antiviral activity of SARS-CoV-2 and its potential effect in regulating the host's immune response. The inhibitory effect of LS against SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero E6 cells was evaluated by using the cytopathic effect (CPE) and plaque reduction assay. The number of virions of SARS-CoV-2 was observed under transmission electron microscope after treatment with LS. Proinflammatory cytokine expression levels upon SARS-CoV-2 infection in Huh-7 cells were measured by real-time quantitative PCR assays. The results showed that LS could significantly inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero E6 cells, and reduce the number of virus particles and it could markedly reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-8, CCL-2/MCP-1 and CXCL-10/IP-10) production at the mRNA levels. Moreover, the expression of the key proteins in the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway was detected by western blot and it was found that LS could inhibit the expression of p-NF-κB p65, p-IκBα and p-p38 MAPK, while increasing the expression of IκBα. These findings indicate that LS could inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virus infection via downregulating the expression of inflammatory cytokines induced virus and regulating the activity of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway in vitro, making its promising candidate treatment for controlling COVID-19 disease.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Antiviral; Liu Shen capsule; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor in response to the articles 'Lianhuaqingwen exerts anti-viral and anti-inflammatory activities against novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)' and 'Liu Shen capsule shows antiviral and anti-inflammatory abilities against novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 via suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway.'.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105289. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105289. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33197600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W., Rollin P.E., Dowell S.F., Ling A., Humphrey C.D., Shieh W., Guarner J., Paddock C.D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J., Cox N., Hughes J.M., LeDuc J.W., Bellini W.J., Anderson L.J. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Zaki A.M., van Boheemen S., Bestebroer T.M., Osterhaus A.D., Fouchier R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;367:1814–1820. - PubMed
-
- Carlos W.G., Dela Cruz C.S., Cao B., Pasnick S., Jamil S. Novel Wuhan (2019-nCoV) coronavirus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

