Mathematical assessment of the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions on curtailing the 2019 novel Coronavirus
- PMID: 32360770
- PMCID: PMC7252217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2020.108364
Mathematical assessment of the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions on curtailing the 2019 novel Coronavirus
Abstract
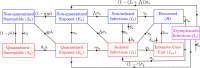
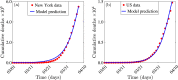
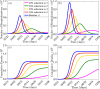
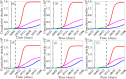
A pandemic of a novel Coronavirus emerged in December of 2019 (COVID-19), causing devastating public health impact across the world. In the absence of a safe and effective vaccine or antivirals, strategies for controlling and mitigating the burden of the pandemic are focused on non-pharmaceutical interventions, such as social-distancing, contact-tracing, quarantine, isolation, and the use of face-masks in public. We develop a new mathematical model for assessing the population-level impact of the aforementioned control and mitigation strategies. Rigorous analysis of the model shows that the disease-free equilibrium is locally-asymptotically stable if a certain epidemiological threshold, known as the reproduction number (denoted by ℛc), is less than unity. Simulations of the model, using data relevant to COVID-19 transmission dynamics in the US state of New York and the entire US, show that the pandemic burden will peak in mid and late April, respectively. The worst-case scenario projections for cumulative mortality (based on the baseline levels of anti-COVID non-pharmaceutical interventions considered in the study) decrease dramatically by 80% and 64%, respectively, if the strict social-distancing measures implemented are maintained until the end of May or June, 2020. The duration and timing of the relaxation or termination of the strict social-distancing measures are crucially-important in determining the future trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic. This study shows that early termination of the strict social-distancing measures could trigger a devastating second wave with burden similar to those projected before the onset of the strict social-distancing measures were implemented. The use of efficacious face-masks (such as surgical masks, with estimated efficacy ≥ 70%) in public could lead to the elimination of the pandemic if at least 70% of the residents of New York state use such masks in public consistently (nationwide, a compliance of at least 80% will be required using such masks). The use of low efficacy masks, such as cloth masks (of estimated efficacy less than 30%), could also lead to significant reduction of COVID-19 burden (albeit, they are not able to lead to elimination). Combining low efficacy masks with improved levels of the other anti-COVID-19 intervention strategies can lead to the elimination of the pandemic. This study emphasizes the important role social-distancing plays in curtailing the burden of COVID-19. Increases in the adherence level of social-distancing protocols result in dramatic reduction of the burden of the pandemic, and the timely implementation of social-distancing measures in numerous states of the US may have averted a catastrophic outcome with respect to the burden of COVID-19. Using face-masks in public (including the low efficacy cloth masks) is very useful in minimizing community transmission and burden of COVID-19, provided their coverage level is high. The masks coverage needed to eliminate COVID-19 decreases if the masks-based intervention is combined with the strict social-distancing strategy.
Keywords: COVID-19; Contact-tracing; Face-mask; Isolation; Mathematical model; Non-pharmaceutical intervention; Quarantine; SARS-CoV-2; Social-distancing.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
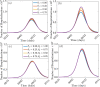
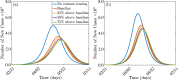
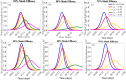

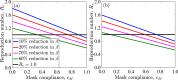
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance. WHO. 2020 https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica.... (Accessed 4 March 2020)
-
- World Health Organization Emergencies, preparedness, response. Pneumonia of unknown origin – China. Dis. Outbreak News. 2020 https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-ch.... (Accessed5 March 2020)
-
- Dong E., Du H., Gardner L. Coronavirus COVID-19 global Cases by Johns Hopkins CSSE. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020 https://gisanddata.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/bda7594...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

