Development and Pilot Test of a Virtual Reality Respiratory Biofeedback Approach
- PMID: 32361963
- PMCID: PMC7391394
- DOI: 10.1007/s10484-020-09468-x
Development and Pilot Test of a Virtual Reality Respiratory Biofeedback Approach
Abstract
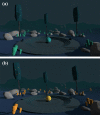
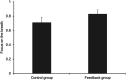
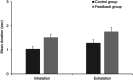
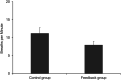
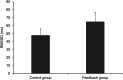
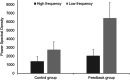
Breathing exercises with biofeedback have benefits over breathing exercises without biofeedback. However, the traditional measurement of respiratory signals that is required as part of feeding back the breath incurs high cost and effort. We propose a novel virtual reality (VR) based approach to respiratory biofeedback that utilizes the positionally tracked hand controllers integrated into modern VR systems to capture and feedback the respiration-induced abdominal movements. In a randomized controlled laboratory study, we investigated the feasibility and efficacy of the developed biofeedback algorithm. In total, 72 participants performed a short breathing exercise in VR with or without respiratory biofeedback. The feedback integration resulted in a satisfactory user experience, a heightened breath awareness, a greater focus on slow diaphragmatic breathing and an increased respiratory sinus arrhythmia. This evidences that the novel biofeedback approach is low-cost, unobtrusive, usable and effective in increasing breath awareness and promoting slow diaphragmatic breathing in the context of VR-based breathing exercises. Future studies need to investigate the broader applicability and long-term effects.
Keywords: Abdominal breathing; Biofeedback; Diaphragmatic breathing; Respiratory biofeedback; Respiratory sinus arrhythmia; Virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychological Association. (2018). Stress in America: Generation Z. Stress in America™ Survey. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/stress/2018/stress-gen-z.pdf.
-
- Bhandari, R., Parnandi, A., Shipp, E., Ahmed, B., & Gutierrez-Osuna, R. (2015, May). Music-based respiratory biofeedback in visually-demanding tasks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression (pp. 78–82). Los Angeles, CA: Baton Rouge.
-
- Burg JM, Michalak J. The healthy quality of mindful breathing: Associations with rumination and depression. Cognitive Therapy and Research. 2011;35:179–185. doi: 10.1007/s10608-010-9343-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

