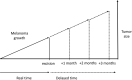
Estimated effect of COVID-19 lockdown on melanoma thickness and prognosis: a rate of growth model
- PMID: 32362041
- PMCID: PMC7267312
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.16555
Estimated effect of COVID-19 lockdown on melanoma thickness and prognosis: a rate of growth model
Figures
References
-
- Phelan AL, Katz R, Gostin LO. The novel coronavirus originating in Wuhan, China: challenges for Global Health Governance. J Am Med Assoc 2020; 323: 709. - PubMed
-
- Grob JJ, Richard MA, Gouvernet J et al. The kinetics of the visible growth of a primary melanoma reflects the tumor aggressiveness and is an independent prognostic marker: a prospective study. Int J Cancer 2002; 102: 34–38. - PubMed
-
- Lin MJ, Mar V, McLean C, Kelly JW. An objective measure of growth rate using partial biopsy specimens of melanomas that were initially misdiagnosed. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014; 71: 691–697. - PubMed
-
- Tejera‐Vaquerizo A, Barrera‐Vigo MV, López‐Navarro N, Herrera‐Ceballos E. Growth rate as a prognostic factor in localized invasive cutaneous melanoma. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol 2010; 24: 147–154. - PubMed
-
- Nagore E, Martorell‐Calatayud A, Botella‐Estrada R, Guillén C. Growth rate as an independent prognostic factor in localized invasive cutaneous melanoma. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol 2011; 25: 618–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical