In silico study the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor of COVID-19 by Ammoides verticillata components harvested from Western Algeria
- PMID: 32362217
- PMCID: PMC7232889
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1763199
In silico study the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor of COVID-19 by Ammoides verticillata components harvested from Western Algeria
Abstract
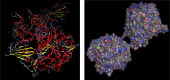
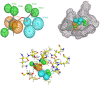
The objective of this present study is to focus on the in silico study to screen for an alternative drug that can block the activity of the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a receptor for SARS-CoV-2, potential therapeutic target of the COVID-19 virus using natural compounds (Isothymol, Thymol, Limonene, P-cymene and γ-terpinene) derived from the essential oil of the antiviral and antimicrobial plant Ammoides verticillata (Desf.) Briq. which is located in the occidental Algeria areas. This study reveals that Isothymol, a major component of this plant, gives the best docking scores, compared to, the co-crystallized inhibitor β-D-mannose of the enzyme ACE2, to Captropil drug as good ACE2 inhibitor and to Chloroquine antiviral drug also involved in other mechanisms as inhibition of ACE2 cellular receptor. In silico (ADME), drug-likeness, PASS & P450 site of metabolism prediction, pharmacophore Mapper showed that the compound Isothymol has given a good tests results compared to the β-D-mannose co-crystallized inhibitor, to Captopril and Chloroquine drugs. Also the other natural compounds gave good results. The Molecular Dynamics Simulation study showed good result for the Isotymol- ACE2 docked complex. This study revealed for the first time that Isothymol is a functional inhibitor of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity and the components of essential oils Ammoides verticillata can be used as potential inhibitors to the ACE2 receptor of SARS-CoV-2.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: Ammoides verticillata; Angiotensin converting enzyme 2; COVID-19; isothymol; molcular docking.
Figures



References
-
- Abdelouahid D. E., & Bekhechi C. (2002). Pouvoir antimicrobien de l’huile essentielle d’Ammoïdes verticillata (Nûnkha). Biologie et Santé, 4, 91–100.
-
- Avesina A. (1985). Law in medecine (2nd éd.). Soroush Press; pp 187.
-
- Awan F., Obaid A., Ikram A., & Janjua H. (2017). Mutation-structure-function relationship based integrated strategy reveals the potential impact of deleterious missense mutations in autophagy related proteins on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): A comprehensive informatics approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(1), 139. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010139 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
