Pacemaker Implantation After Balloon- or Self-Expandable Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 32362220
- PMCID: PMC7428568
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.015896
Pacemaker Implantation After Balloon- or Self-Expandable Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Aortic Stenosis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Pacemaker Implantation After Balloon- or Self-Expandable Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Aortic Stenosis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jul 7;9(13):e014562. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014562. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32538244 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
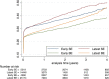
Background The incidence of conduction abnormalities requiring permanent pacemaker implantation (PPI) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) with early and later generation prostheses remains debated. Methods and Results Based on the administrative hospital-discharge database, we collected information for all patients treated with TAVR between 2010 and 2019 in France. We compared the incidence of PPI after TAVR according to the type and generation of valve implanted. A total of 49 201 patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR using the balloon-expandable (BE) Edwards SAPIEN valve (early Sapien XT and latest Sapien 3) or the self-expanding (SE) Medtronic CoreValve (early CoreValve and latest Evolut R) were found in the database. Mean (SD) follow-up was 1.2 (1.5 years) (median [interquartile range] 0.6 [0.1-2.0] years). PPI after the procedure was reported in 13 289 patients, among whom 11 010 (22.4%) had implantation during the first 30 days. In multivariable analysis, using early BE TAVR as reference, adjusted odds ratio (95% CI) for PPI during the first 30 days was 0.88 (0.81-0.95) for latest BE TAVR, 1.40 (1.27-1.55) for early SE TAVR, and 1.17 (1.07-1.27) for latest SE TAVR. Compared with early BE TAVR, the adjusted hazard ratio for PPI during the whole follow-up was 1.01 (0.95-1.08) for latest BE TAVR, 1.30 (1.21-1.40) for early SE TAVR, and 1.25 (1.18-1.34) for latest SE TAVR. Conclusions In patients with aortic stenosis treated with TAVR, our systematic analysis at a nationwide level found higher rates of PPI than previously reported. BE technology was independently associated with lower incidence rates of PPI both at the acute and chronic phases than SE technology. Recent generations of TAVR were not independently associated with different rates of PPI than early generations during the overall follow-up.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; pacemaker; transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pacemaker Implantation After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Necessary Evil Perhaps But Are We Making Progress?J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 May 5;9(9):e016700. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016700. Epub 2020 May 2. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32362173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nguyen V, Michel M, Eltchaninoff H, Gilard M, Dindorf C, Iung B, Mossialos E, Cribier A, Vahanian A, Chevreul K, et al. Implementation of transcatheter aortic valve replacement in France. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:1614–1627. - PubMed
-
- Deharo P, Bisson A, Herbert J, Lacour T, Saint Etienne C, Grammatico‐Guillon L, Porto A, Collart F, Bourguignon T, Cuisset T, et al. Impact of Sapien 3 balloon‐expandable versus evolut R self‐expandable transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with aortic stenosis: data from a nationwide analysis. Circulation. 2020;141:260–268. - PubMed
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack MJ, Makkar RR, Svensson LG, Kodali SK, Thourani VH, Tuzcu EM, Miller DC, Herrmann HC, et al. Transcatheter or surgical aortic‐valve replacement in intermediate‐risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1609–1620. - PubMed
-
- Mack MJ, Leon MB, Thourani VH, Makkar R, Kodali SK, Russo M, Kapadia SR, Malaisrie SC, Cohen DJ, Pibarot P, et al.; PARTNER 3 Investigators . Transcatheter aortic‐valve replacement with a balloon‐expandable valve in low‐risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1695–1705. - PubMed
-
- Reardon MJ, Adams DH, Kleiman NS, Yakubov SJ, Coselli JS, Deeb GM, Gleason TG, Lee JS, Hermiller JB Jr, Chetcuti S, et al. 2‐year outcomes in patients undergoing surgical or self‐expanding transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:113–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

